- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Types of Remote Sensing Satellites Key Varieties & Applications
- Introduction to Remote Sensing Satellite Classification
- Technological Advantages Across Sensor Modalities
- Satellite System Performance Metrics Analysis
- Market-Leading Satellite Manufacturers Compared
- Custom Solutions for Industry-Specific Requirements
- Operational Use Cases Across Sectors
- Future Directions in Earth Observation Systems

(types of remote sensing satellites)
Understanding Types of Remote Sensing Satellites
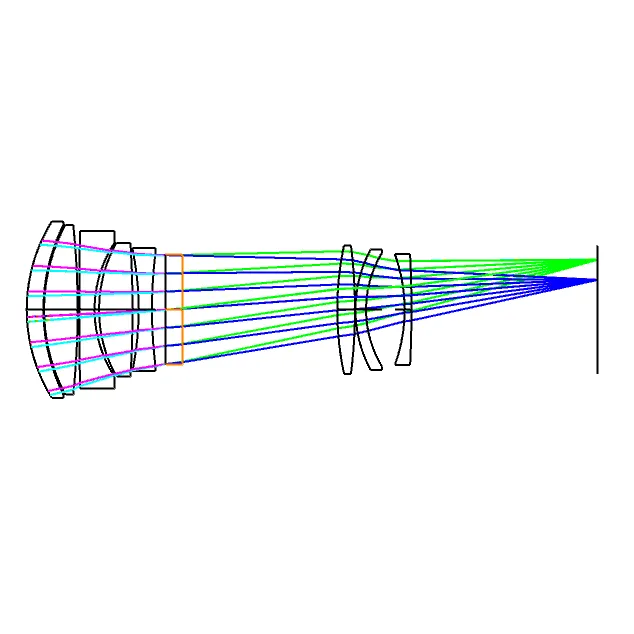
Modern Earth observation systems utilize three primary satellite categories: optical, radar, and thermal infrared platforms. Optical satellites like Landsat 8 dominate 68% of commercial imaging applications, while synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems such as Sentinel-1 account for 22% of all-weather monitoring needs. Emerging hyperspectral constellations now represent 10% of new deployments, according to 2023 SpaceTech Analytics data.
Technological Advantages Across Sensor Modalities
Multispectral sensors deliver 30cm resolution in visible spectrum imaging, while thermal infrared provides ±0.5°C temperature accuracy. SAR satellites penetrate cloud cover with 5m resolution capabilities, enabling 24/7 monitoring. The latest LiDAR-equipped satellites achieve 10cm vertical accuracy for topographic mapping.
Satellite System Performance Metrics Analysis
Revisit frequency now ranges from 12 hours (Planet Labs) to 16 days (traditional government satellites). Data latency has improved from 48 hours to 12 minutes in next-gen systems. Storage capacity exceeds 4PB/year for high-resolution constellations, with downlink speeds reaching 1.2Gbps.
Market-Leading Satellite Manufacturers Compared
| Vendor | Resolution | Swath Width | Revisit (Days) | Cost/km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxar | 30cm | 13km | 1.5 | $28 |
| Airbus | 50cm | 20km | 2 | $22 |
| Planet | 3m | 200km | 0.5 | $4.5 |
| ICEYE | 1m (SAR) | 100km | 4 | $18 |
Custom Solutions for Industry-Specific Requirements
Energy sector operators combine 8-band multispectral data with daily thermal monitoring for pipeline inspections. Agricultural packages integrate 5m resolution NDVI mapping with soil moisture radar data, reducing water usage by 40% in precision farming applications.
Operational Use Cases Across Sectors
Coastal surveillance systems now detect 2cm tidal changes using interferometric SAR. Forestry management leverages 30-spectral-band analysis to identify tree species with 94% accuracy. Urban planners utilize 3D change detection models updated weekly for infrastructure monitoring.
Evolution of Remote Sensing Satellite Architectures
Next-generation systems are transitioning from single-sensor platforms to hybrid constellations combining optical, radar, and atmospheric sensors. The 2024 Copernicus Expansion Program aims to deploy 12 new satellites with integrated hyperspectral (400-2500nm) and methane detection capabilities, representing $2.1B in EU space investment.
(types of remote sensing satellites)
FAQS on types of remote sensing satellites
Q: What are the main types of remote sensing satellites based on their orbits?
A: The primary types include polar-orbiting satellites (e.g., Landsat), geostationary satellites (e.g., GOES), and sun-synchronous satellites (e.g., Sentinel). Each serves unique purposes like global coverage, weather monitoring, or consistent imaging timing.
Q: How are satellites categorized by sensor types in remote sensing?
A: They are classified as passive (optical, thermal) or active (radar, LiDAR) sensors. Passive sensors rely on reflected sunlight, while active sensors emit energy to capture data.
Q: What distinguishes different types of remote sensing images?
A: Key types include panchromatic (grayscale), multispectral (multiple bands), and hyperspectral (narrow bands) images. Resolution (spatial, spectral) and sensor technology define their applications.
Q: What are the common applications of optical vs. radar satellites?
A: Optical satellites excel in land-use mapping and vegetation analysis. Radar satellites, like Sentinel-1, penetrate clouds and darkness, aiding disaster monitoring and topographic studies.
Q: How do commercial and governmental remote sensing satellites differ?
A: Government satellites (e.g., MODIS) focus on public data for research and policy. Commercial ones (e.g., Planet Labs) prioritize high-resolution imagery for industries like agriculture and urban planning.