- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
SpaceNavi FAQ
Welcome to SpaceNavi's FAQ page! Here, you’ll find answers to common questions about our high-performance satellite manufacturing, component testing, remote sensing services, and customized solutions. If you need further assistance, feel free to contact us!
-
What Are The Main Applications Of Satellites?
Satellites are used for communication, Earth observation, navigation (GPS), weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, military surveillance, and scientific research. They also support disaster management, remote sensing, and commercial applications like broadcasting and internet services. -
What Types Of Optical Cameras Are Used In Satellites And Uavs?
Optical cameras include high-resolution imaging cameras, multispectral and hyperspectral sensors, infrared cameras, and thermal imaging systems. These cameras are used for remote sensing, land mapping, agricultural monitoring, and defense applications. -
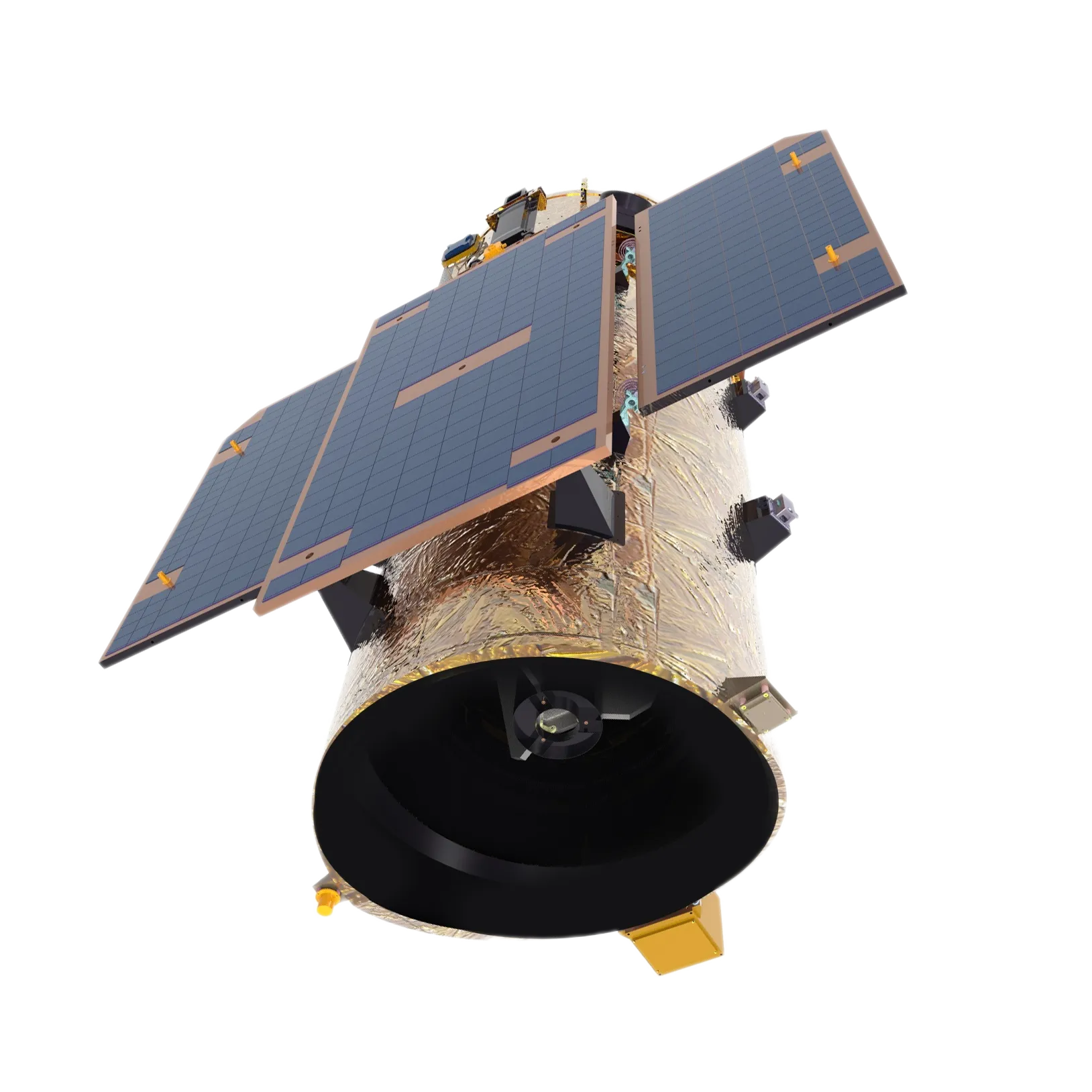
What Are The Key Components Of A Satellite Or Uav?
Essential components include power systems (solar panels, batteries), communication modules, cameras, sensors, propulsion systems, and control units. These ensure stable operation, data transmission, and efficient mission performance. -
How Is Satellite Data Used In Different Industries?
Satellite data supports agriculture (crop monitoring), environmental studies (deforestation tracking, climate change analysis), urban planning, disaster management (flood and wildfire prediction), security and defense (surveillance), and industrial applications like mining and oil exploration. -
How Do Satellites Capture High-resolution Images?
Satellites use advanced optical cameras with high-precision lenses and sensors. They capture images in different spectral bands, allowing detailed analysis of land, water, and atmospheric conditions. -
What Is The Difference Between Multispectral And Hyperspectral Imaging?
Multispectral imaging captures data in a few spectral bands, while hyperspectral imaging collects hundreds of bands, providing more detailed insights for applications like mineral exploration, agriculture, and medical imaging. -
How Long Do Satellites Typically Last?
The lifespan depends on the mission type. Communication satellites usually last 10-15 years, while Earth observation satellites function for 5-10 years. The lifespan is influenced by radiation exposure, fuel capacity, and system wear.