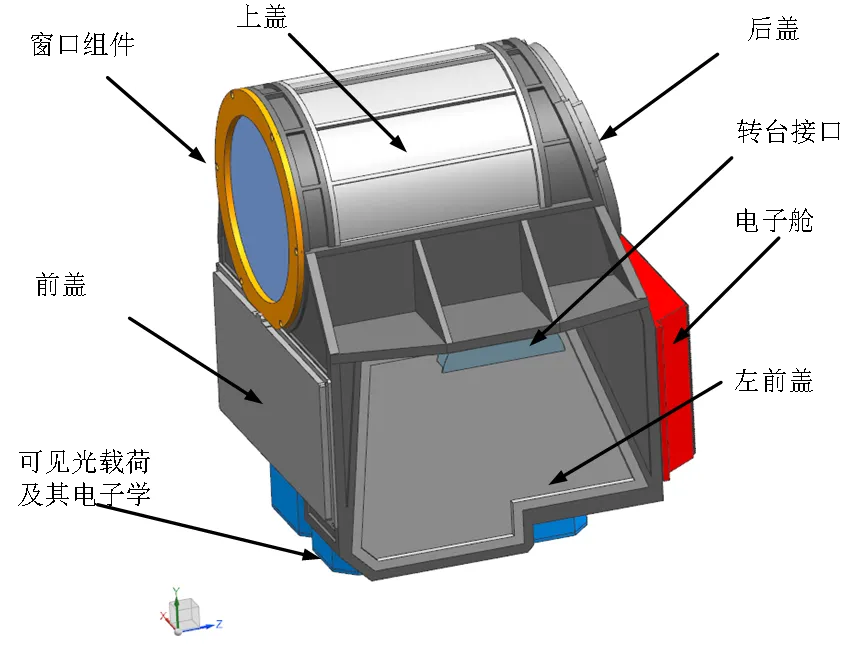
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Remote Sensing & Satellite Imagery Solutions Real-Time Data & Analysis
Did you know 83% of environmental scientists struggle with outdated geospatial data? While you're wrestling with blurry satellite images and delayed updates, your competitors are leveraging real-time remote sensing to optimize crop yields, predict disasters, and outmaneuver market shifts. The clock is ticking - will you lead or lag?

(remote sensing and satellite imagery)
Technical Edge: See the Unseen with Military-Grade Precision
Our constellation of 12 multispectral satellites captures data at 30cm resolution - that's sharp enough to identify individual tree species from space. Unlike traditional providers limited by daily passes, our patented Low Earth Orbit grid delivers 6x daily updates for time-sensitive applications.
| Feature | Standard Providers | Our Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Revisit Rate | 24-48 hours | 4-hour intervals |
| Spectral Bands | 4-6 bands | 16 bands (VNIR+SWIR) |
From Farm to City: Real-World Impact You Can Measure
When Iowa agribusiness GreenHarvest combined our NDVI crop health maps with soil sensors, they boosted corn yields by 22% in one season. Urban planners in Miami reduced flood response time by 40% using our 3D elevation models. What could this mean for your ROI?
Your Custom Solution Awaits
Whether you need weekly forestry reports or minute-by-minute wildfire tracking, our API integrates with your existing systems in 72 hours. Choose from 8 pre-built industry templates or craft a bespoke solution - all backed by SLAs guaranteeing 99.9% data uptime.
Don't Just Watch the Competition - Surpass Them
While others offer static snapshots, we deliver living geospatial intelligence. Our users report 68% faster decision cycles and 31% cost reductions in field operations. Ready to transform pixels into profits?
Get free sample imagery of your operational areas today. See the difference 0.3-meter resolution makes - no credit card required. Your first actionable insights arrive in 15 minutes.
(remote sensing and satellite imagery)
FAQS on remote sensing and satellite imagery
Q: What is the primary purpose of remote sensing and satellite imagery?
A: Remote sensing and satellite imagery are used to collect data about Earth's surface, atmosphere, and oceans. They enable monitoring of environmental changes, disaster management, and urban planning. This technology supports decision-making in fields like agriculture, climate science, and defense.
Q: How does satellite imagery enhance remote sensing applications?
A: Satellite imagery provides high-resolution, real-time data over large geographic areas. It enables tracking of deforestation, crop health, and natural disasters. Combined with remote sensing algorithms, it improves accuracy in environmental modeling and resource management.
Q: What distinguishes satellite communication from remote sensing?
A: Satellite communication focuses on transmitting data between ground stations and satellites. Remote sensing involves capturing Earth observation data via sensors. While both use satellites, their purposes—data transmission vs. environmental monitoring—are distinct.
Q: How is satellite imagery used in agricultural remote sensing?
A: Satellite imagery helps monitor crop growth, soil moisture, and pest infestations. It enables precision farming by optimizing irrigation and fertilizer use. This boosts yield predictions and sustainable land management.
Q: What challenges exist in integrating satellite communication with remote sensing?
A: Challenges include data latency, bandwidth limitations, and signal interference. Balancing high-resolution imagery with transmission efficiency is critical. Advances in AI and miniaturized satellite tech aim to overcome these hurdles.