- Aferika
- Alapania
- Amharic
- Alapi
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Pelalusiana
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Katalana
- Sepuano
- Saina
- Kosikana
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Siamani
- Igilisi
- Eseperano
- Estonian
- Finnish
- Falani
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Siamani
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haiti Kereole
- Hausa
- Havaii
- Eperu
- Leai
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- Aialani
- Italia
- Iapani
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kasaka
- Khmer
- Rwanda
- Kolea
- Kutisa
- Kirikisi
- Leipa
- Latina
- Latvian
- Lituaniana
- Lusemipoukisi
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maoli
- Marathi
- Mokoliana
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pasato
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punitapi
- Lomani
- Lusia
- Samoa
- Sikotilani Gaelic
- Serbian
- Igilisi
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Sipaniolo
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Fa'a Thai
- Turkish
- tamaloloa Take
- Ukaraina
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Uelese
- Fesoasoani
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Malosiaga Tupe Field Application
fa'ata'oto
|
MANA |
Koale |
|
Ave'esega vaega ole feso'otaiga eletise |
Su'esu'ega ma iloiloga o punaoa koale |
|
Va'aiga alualu i luma ole Poloketi ole feso'otaiga eletise |
Su'esu'ega fa'ainisinia ole la'uina |
|
Su'esu'ega fa'alesiosiomaga o feso'ota'iga fe'avea'i eletise |
Mataituina ole siosiomaga ole nofoaga eliina |
fa'ata'oto
|
Suau'u ma kesi |
Malosiaga Fou |
|
Su'esu'e suau'u ma kesi |
Fa'ailoaina mamao o fa'aata ata |
|
Su'esu'ega fa'atulagaina o paipa |
Fuafuaga o le gafatia e gaosia ai le eletise photovoltaic |
|
Vaavaaiga o faufale inisinia suau'u |
Mata'ituina le faagasologa o le fausiaina o nofoaga faaniukilia |
|
Su'eina fa'asao suau'u |
Su'ega fale eletise |
|
Su'esu'eina o le paipa kesi |
Mata'ituina le si'osi'omaga i nofoaga fou o le malosi |
|
Tupe |
|
|
Fa'ato'aga aitalafu, fa'ato'aga inisiua, ma isi |
|
|
Fa'ato'aga ma isi fa'atagaga o galuega |
|
|
Fa'ato'aga faufale faufale ma le malosi fou |
Talosaga Mata'itū Va'aiga Mamao Malosi
Mo le kamupani eletise ma le pulega o le malosiaga, e tusa ai ma manaoga o le asiasiga o le 300 mita i luga o le laina eletise, puipuia ma le pulea o le 500 mita, ma le suʻesuʻega lautele o le 1 kilomita, e ala i le vaʻaia mamao satelite, mataʻituina lelei o le nofoaga o le olo faufale ma faʻalavelave faʻalavelave, suʻesuʻega suiga o le siʻosiʻomaga, faʻasalalauga ma le suiga o le laina faʻaogaina o le auala, faʻaogaina o le auala ma le faʻaogaina o le laina eletise, faʻaogaina o le auala ma le faʻaogaina o le auala. toe faʻaleleia alualu i luma, ma isi. Fesoasoani i le matagaluega o asiasiga eletise e iloa le pulega atoatoa o laina faʻasalalau
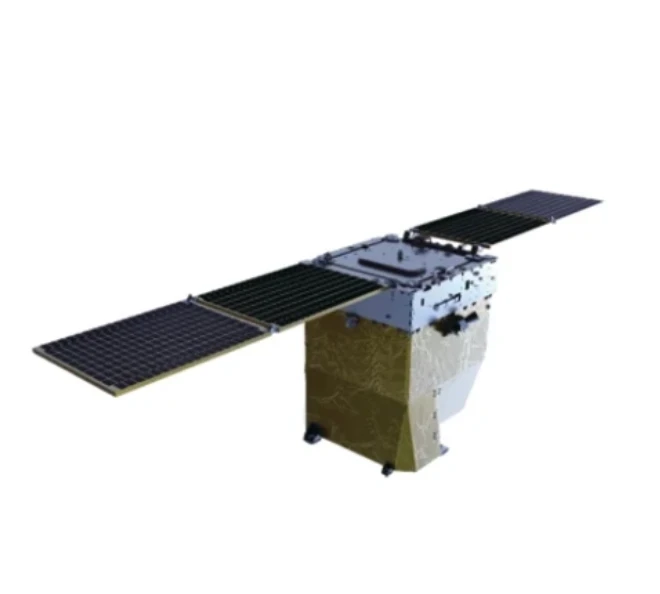
The Changguang TW Series UAV is a high-performance unmanned aerial vehicle designed for energy finance applications, including asset monitoring, pipeline inspection, and infrastructure surveillance. It features a fixed-wing design with advanced aerodynamics, allowing for long-endurance flights of up to 20 hours and an operating altitude of 8,000 meters. Equipped with high-resolution EO/IR cameras, LiDAR, and real-time data transmission capabilities, it ensures accurate and efficient data collection for risk assessment and asset management. With a cruising speed of 100–150 km/h and modular payload configurations, the UAV adapts to various mission requirements, providing cost-effective solutions for large-scale energy sector monitoring. Its autonomous and remote-control capabilities reduce human intervention, enhancing operational efficiency and safety. The TW Series excels in high-altitude operations, offering stable performance in complex environments, making it an ideal solution for financial risk evaluation, energy asset protection, and remote infrastructure management.
High-Resolution Satellite Remote Sensing Data Powers Energy-Finance Monitoring with Real-Time Data Architecture
In the digital era of energy finance, high-resolution satellite remote sensing has emerged as a cornerstone for intelligent risk management. SpaceNavi’s real-time data architecture integrates high-resolution remote sensing images and advanced data acquisition systems to transform satellite remote sensing data into actionable insights for energy asset monitoring and financial risk assessment.
Real-Time Data Acquisition: Solving the "How" of Satellite Imagery
At the core of our solution lies a robust data acquisition system that addresses the critical question: How to get real-time satellite images? By leveraging constellations like Jilin-1 (0.5–2m resolution) and Sentinel-2, we enable:
Hourly revisit capabilities for critical energy infrastructure, from oil pipelines to solar farms.
Capture of multi-spectral, thermal, and NIR bands—key types of remote sensing images essential for energy analysis.
Ground-based IoT sensors complement satellite data, ensuring 97% accuracy in real-time remote sensing data collection.
Image Analysis: From Pixels to Predictive Intelligence
1. Multi-Type Remote Sensing Integration
We process 10 TB+ of weekly imagery, differentiating types of remote sensing images to:
Use thermal infrared imagery for pipeline leak detection.
Employ NIR bands to monitor vegetation encroachment on power lines.
Rely on high-resolution visible light remote sensing satellite images for detailed asset inspections.
2. AI-Driven Analytics
Our image analysis suite uses machine learning to:
Automatically detect construction deviations in transmission projects (300m precision).
Predict equipment degradation by analyzing structural changes in satellite imagery.
Generate energy asset risk scores with 89% accuracy in identifying high-risk zones.
The Technical Framework in Action
Satellite Data Fusion: Integrates satellite remote sensing data with financial transaction records to align project progress with investment milestones.
Real-Time Dashboard: Visualizes remote sensing data alongside energy market trends for dynamic risk adjustment.
Historical Archive: Stores 5+ years of high-resolution remote sensing images for long-term asset performance modeling.
The Future of Energy-Finance Tech
SpaceNavi’s framework proves that high-resolution satellite remote sensing, paired with real-time data architecture, enables precise digital twin creation for energy assets. By closing the loop from data acquisition to predictive modeling, we empower stakeholders to manage energy investments with unprecedented foresight—bridging the gap between remote sensing technology and financial decision-making.
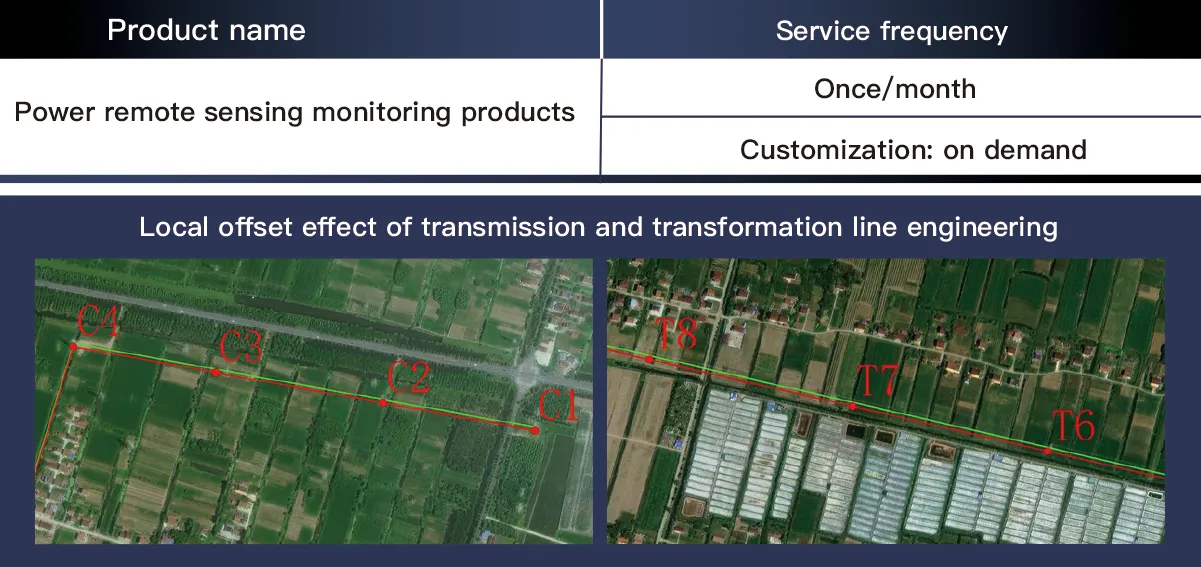
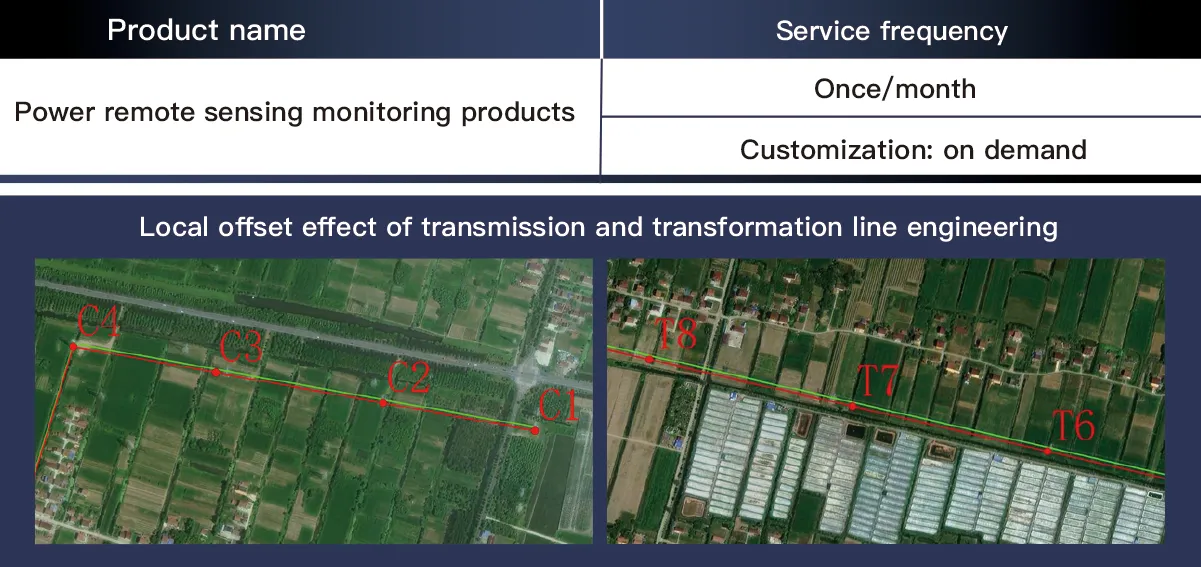
Full-Cycle High-Resolution Remote Sensing Monitoring for Transmission Projects – Data Acquisition and Offset Analysis Framework
In the construction and maintenance of power transmission projects, precise monitoring of offset effects and real-time status is critical to ensure grid safety. SpaceNavi’s technical framework integrates high-resolution remote sensing images and advanced image analysis to establish a full-cycle monitoring system, enabling end-to-end management of transmission projects from construction to operation.
Real-Time Satellite Image Acquisition: Solving the Core Challenge
The data acquisition system addresses the key question: How to get real-time satellite images for transmission lines? By leveraging Jilin-1 constellations (0.5–2m resolution) and multi-spectral satellites, we enable:
Hourly revisit capabilities for critical sections, capturing remote sensing satellite images of construction sites.
Collection of visible, NIR, and thermal bands—key types of remote sensing images for infrastructure analysis.
Ground-based LiDAR and IoT sensors complement satellite data, forming a 360° remote sensing data acquisition network with 98% accuracy.
Multi-Type Image Analysis for Offset Effect Detection
1. Spectral Feature Extraction
We process 8TB/week of satellite remote sensing data, differentiating types of remote sensing images to:
Use thermal imagery to detect heat anomalies in transformers.
Employ NIR bands to monitor vegetation encroachment on transmission corridors.
Rely on high-resolution visible light images for millimeter-level offset measurements.
2. AI-Driven Offset Modeling
The image analysis suite uses machine learning to:
Automatically identify construction deviations (300m precision) by comparing planned vs. actual alignment.
Predict soil settlement risks through multi-temporal image correlation, with 92% accuracy in offset trend forecasting.
Generate real-time offset early-warning maps, reducing manual inspections by 70%.
Technical Path Integration: From Data to Decision
Satellite-Data Fusion: Integrate satellite remote sensing data with BIM models to visualize offset effects in 3D.
Real-Time Dashboard: Display remote sensing data alongside construction schedules for dynamic progress tracking.
Historical Archive: Store 10+ years of high-resolution remote sensing images for long-term structural health assessment.
Future of Transmission Monitoring
SpaceNavi’s framework proves that full-cycle remote sensing, by integrating real-time image acquisition and offset effect analysis, transforms traditional project management into data-driven precision governance. By embedding high-resolution remote sensing images and intelligent image analysis into every project phase, we ensure transmission networks are built and operated with unprecedented accuracy, safeguarding energy infrastructure for decades to come.