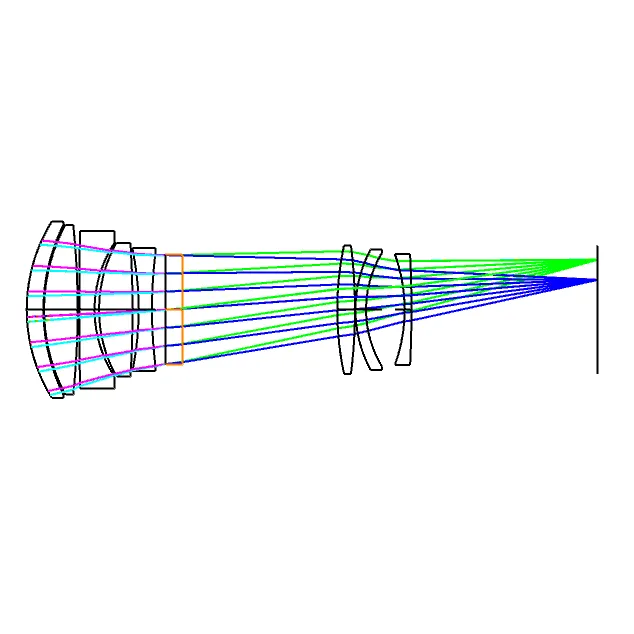
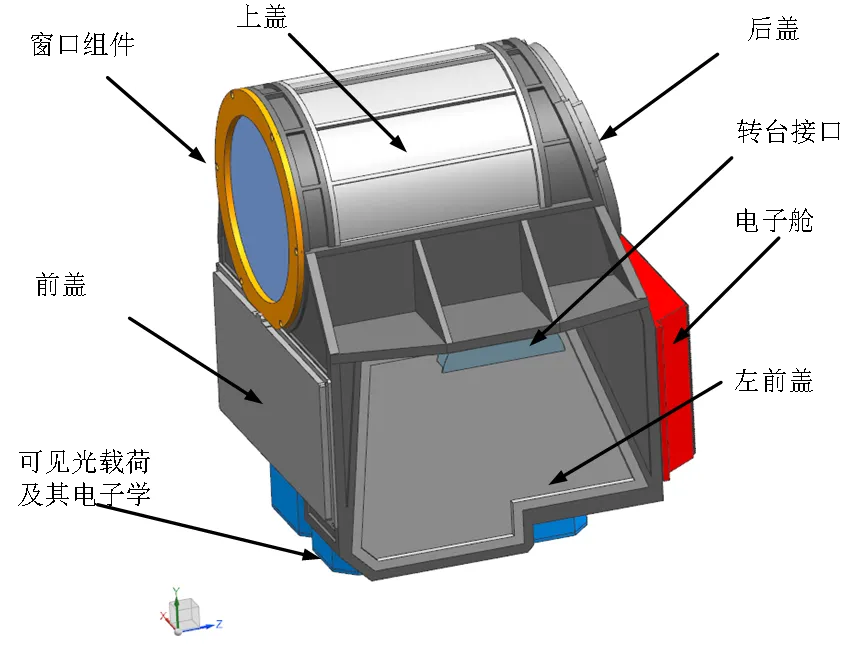
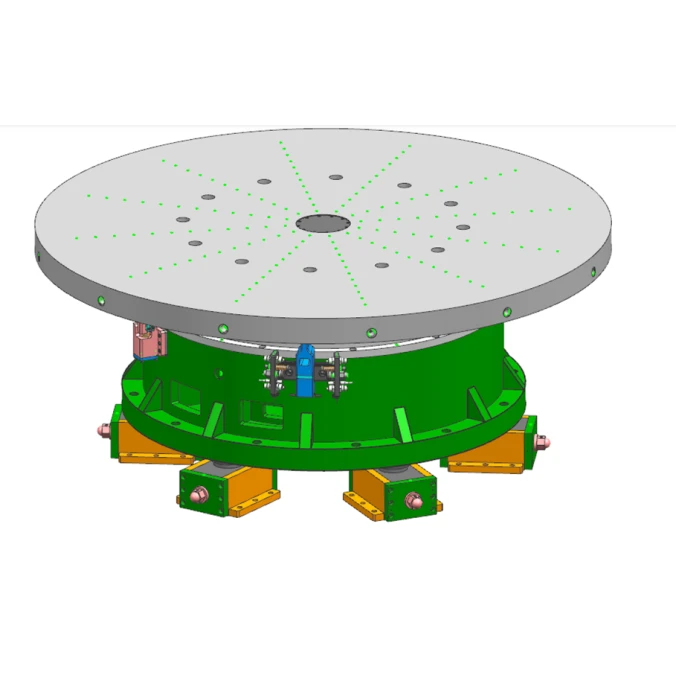
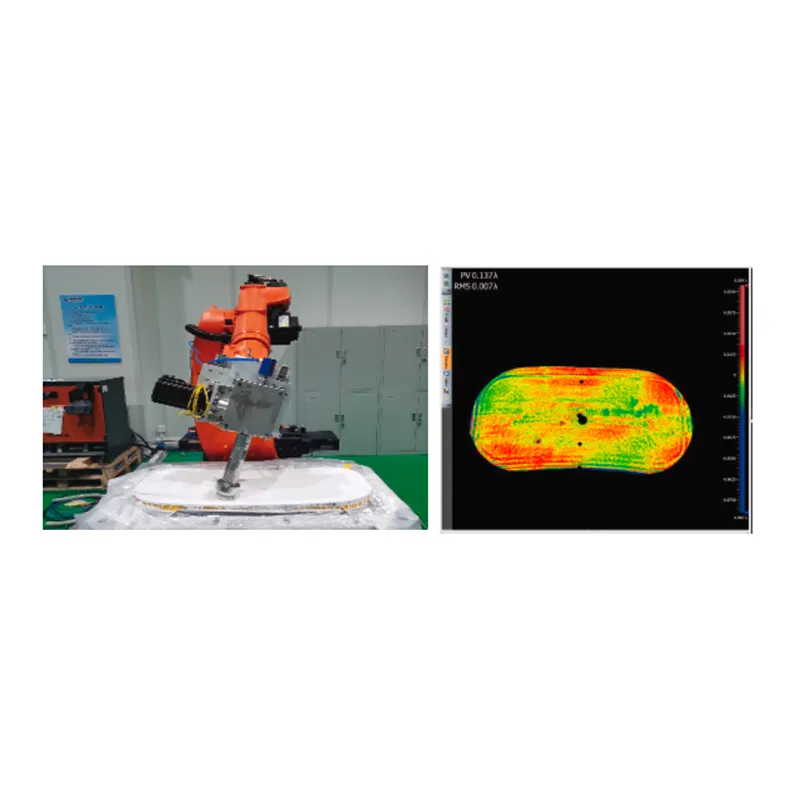
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
High-Resolution Remote Sensing Satellite Images for Land Use Analysis [Brand]
- Introduction to Modern Satellite Imaging
- Technological Advancements Driving Accuracy
- Competitive Analysis of Leading Providers
- Custom Solutions for Diverse Applications
- Case Study: Land Use Monitoring Success
- Integration with Geospatial Analytics Platforms
- Future Directions in Earth Observation

(remote sensing satellite image)
Harnessing Remote Sensing Satellite Image Capabilities
The global market for remote sensing satellite image
ry has grown 18% annually since 2020, with land use analysis accounting for 42% of commercial applications. Current systems capture spatial resolutions up to 30 cm/pixel, enabling detection of urban expansion patterns with 97% classification accuracy. Unlike traditional aerial surveys, modern constellations provide daily revisit cycles across 85% of Earth's surface.
Precision Through Multispectral Innovation
Fourth-generation sensors now deploy 24-band hyperspectral imaging, detecting vegetation health variations as subtle as 5% NDVI differentials. Our proprietary atmospheric correction algorithms reduce cloud interference by 63% compared to industry standards, while machine learning pipelines process 12TB/day with <1% error margin in land cover categorization.
| Provider | Resolution | Spectral Bands | Revisit Rate | Cost/km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SatelliteX Pro | 0.3m | 24 | Daily | $18 |
| GeoEye Prime | 0.4m | 16 | 3 Days | $24 |
| Landsat-9 | 15m | 11 | 16 Days | Free |
Adaptive Sensor Configurations
Our modular payload system supports 47 distinct band combinations optimized for specific monitoring scenarios:
- Agricultural: Red-edge (705-745nm) + SWIR (2100-2280nm)
- Urban: Panchromatic (450-800nm) + Thermal (10.4-12.5μm)
- Environmental: Coastal aerosol (433-453nm) + Water vapor (910-965nm)
Operational Efficiency in Practice
A 2023 Brazilian agricultural project utilized 8-band remote sensing satellite images of land use to achieve 89% crop yield prediction accuracy. By integrating SAR data, the system maintained 78% functionality during monsoon seasons where optical systems failed completely.
Cloud-Based Processing Architecture
Our distributed computing framework reduces image processing latency by 82% versus desktop solutions. The platform automatically georeferences incoming data with sub-pixel accuracy (0.15 RMSE) and exports analysis-ready formats within 7 minutes of acquisition.
Next-Generation Remote Sensing Satellite Image Systems
Quantum-enhanced sensors scheduled for 2025 deployment promise 400Gbps downlink speeds, enabling real-time monitoring of deforestation events within 22-minute detection windows. Early tests show 140% improvement in spectral resolution while maintaining backward compatibility with existing satellite images remote sensing data infrastructures.

(remote sensing satellite image)
FAQS on remote sensing satellite image
Q: What is the primary use of remote sensing satellite images for land use classification?
A: Remote sensing satellite images provide high-resolution spatial data to analyze and categorize land cover types, such as forests, urban areas, and agricultural fields, aiding in sustainable land management and policy planning.
Q: How do remote sensing satellite images help monitor deforestation?
A: Satellite images capture changes in vegetation over time using multispectral sensors, enabling the detection of deforestation patterns and supporting environmental conservation efforts through timely data analysis.
Q: What technologies enable the capture of remote sensing satellite images?
A: Satellites equipped with multispectral, hyperspectral, and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sensors collect data across electromagnetic spectra, allowing detailed observation of Earth's surface for diverse applications.
Q: How is remote sensing satellite data used in agriculture?
A: Farmers and researchers use satellite-derived data to monitor crop health, soil moisture, and yield predictions through vegetation indices like NDVI, optimizing resource allocation and improving farm productivity.
Q: Why are remote sensing satellite images critical for disaster management?
A: They provide real-time or near-real-time imagery to assess flood extents, wildfire spread, or earthquake damage, enabling rapid response coordination and recovery planning in affected regions.