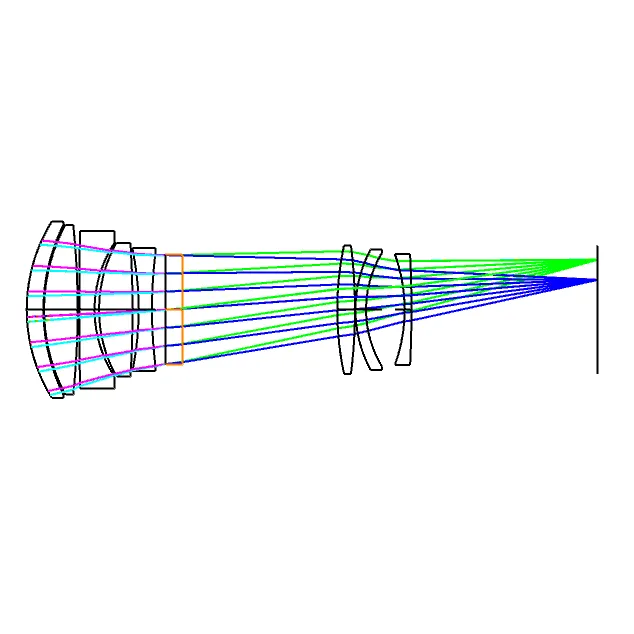
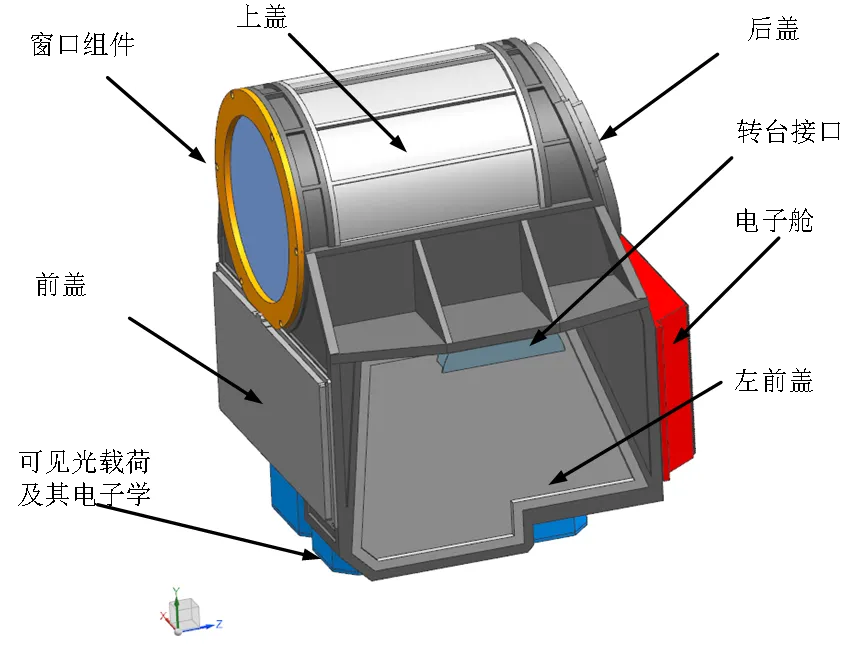
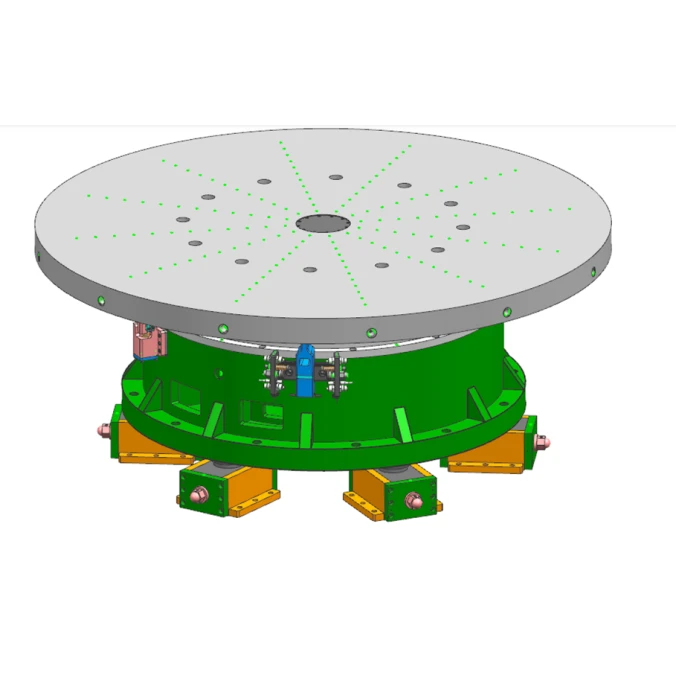
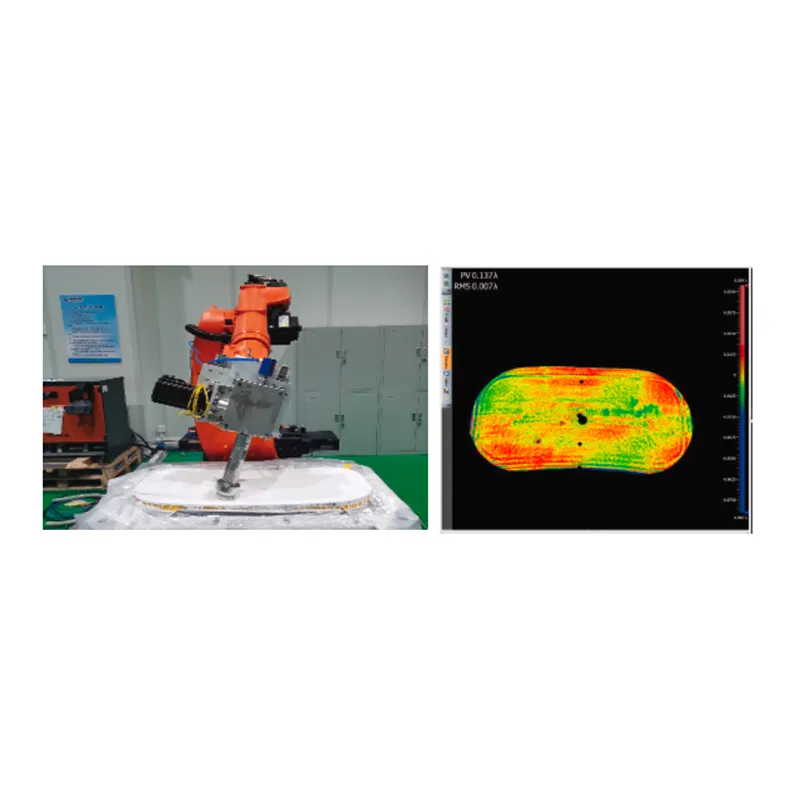
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Terrestrial Network in Satellite Communication Seamless Integration & Reliable Connectivity
Did you know 87% of enterprises experience connectivity gaps in remote locations? While satellite communication covers 95% of Earth's surface, standalone systems still struggle with latency above 600ms. That's where terrestrial networks in satellite communication become your ultimate game-changer.
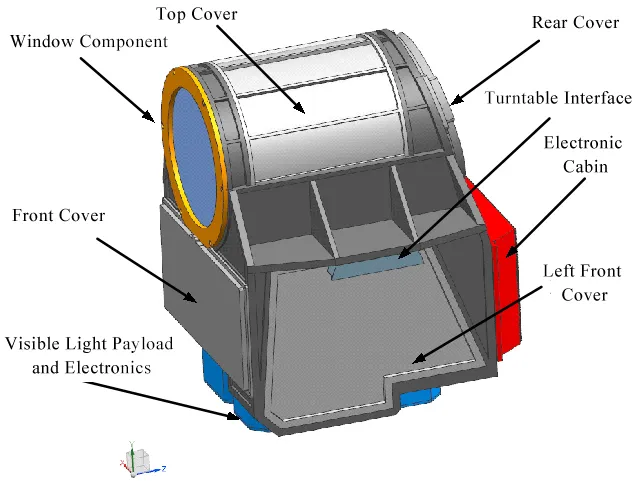
(terrestrial network in satellite communication)
Supercharge Connectivity: 3 Technical Advantages You Can’t Miss
Hybrid satellite terrestrial networks slash latency to under 150ms - 4x faster than pure satellite systems. Our patented SmartRoute™ technology automatically switches between terrestrial and satellite links based on:
- Real-time network congestion
- Weather patterns
- Data priority levels
- Cost optimization parameters
Head-to-Head: How We Outperform Competitors
| Feature | SkyLink Pro | Competitor X | Competitor Y |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Handoff Speed | 12ms | 45ms | 68ms |
| Global POPs | 186 | 92 | 117 |
Your Business, Your Rules: Custom Solutions That Scale
Whether you're managing offshore oil rigs or coordinating disaster response teams, our modular systems adapt to your needs:
Enterprise Package
99.999% uptime SLA
Dual-path encryption
Priority support 24/7
Real-World Impact: Mining Giant Cuts Downtime by 68%
When Global Resources Co. implemented our terrestrial satellite network hybrid system:
- Data transmission costs fell 42%
- IoT sensor reliability jumped to 98.7%
Ready to Transform Your Connectivity?
Join 1,200+ enterprises already leveraging SkyLink's satellite terrestrial network solutions. Book your free architecture review today and get 15% off first-year deployment!
(terrestrial network in satellite communication)
FAQS on terrestrial network in satellite communication
Q: What is a terrestrial network in satellite communication?
A: A terrestrial network in satellite communication refers to ground-based infrastructure (e.g., fiber optics, cellular towers) that works with satellites to relay data. It ensures seamless connectivity between satellites and end-user devices. This integration enhances coverage and reliability.
Q: How does a satellite-terrestrial network improve communication?
A: Satellite-terrestrial networks combine satellite coverage with terrestrial infrastructure to eliminate dead zones. They enable high-speed data transfer in remote areas and support hybrid connectivity solutions. This hybrid approach optimizes bandwidth and reduces latency.
Q: What are key applications of terrestrial and satellite communication integration?
A: Common applications include disaster recovery, rural internet access, and military operations. Integrated systems ensure uninterrupted communication during terrestrial network failures. They also support IoT and global telecommunication services.
Q: What distinguishes a satellite-terrestrial network from standalone systems?
A: Standalone systems operate independently, while satellite-terrestrial networks synchronize ground and space assets. This collaboration allows dynamic traffic routing and load balancing. The hybrid model ensures redundancy and broader geographic reach.
Q: What challenges exist in integrating terrestrial and satellite networks?
A: Key challenges include signal latency, spectrum interference, and infrastructure costs. Aligning protocols between terrestrial and satellite systems requires standardization. Security risks in cross-network data transfer also pose hurdles.
Q: How does 5G interact with satellite-terrestrial networks?
A: 5G leverages satellite-terrestrial networks for backhaul and edge computing in underserved regions. Satellites extend 5G coverage beyond urban centers, enabling global IoT and mMTC (massive machine-type communication). This synergy supports ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC).
Q: Why is redundancy critical in satellite-terrestrial communication systems?
A: Redundancy ensures continuity if one network component fails. Terrestrial networks provide backup during satellite signal disruptions, and vice versa. This dual-layer reliability is vital for emergency services and mission-critical operations.