- Afirika
- Ede Albania
- Amharic
- Larubawa
- Ara Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Ede Bengali
- Ede Bosnia
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Ede Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonia
- Finnish
- Faranse
- Frisia
- Galician
- Georgian
- Jẹmánì
- Giriki
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- Hausa
- ara ilu Hawaiani
- Heberu
- Rara
- Miao
- Ede Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Ede Indonesian
- Irish
- Itali
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kasakh
- Khmer
- Ede Rwandan
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kirgisi
- Iṣẹ-ṣiṣe
- Latin
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Èdè Malta
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Mianma
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scotland Gaelic
- Ede Serbia
- English
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Somali
- Sipeeni
- Ede Sundan
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Tọki
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbekisi
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Egba Mi O
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
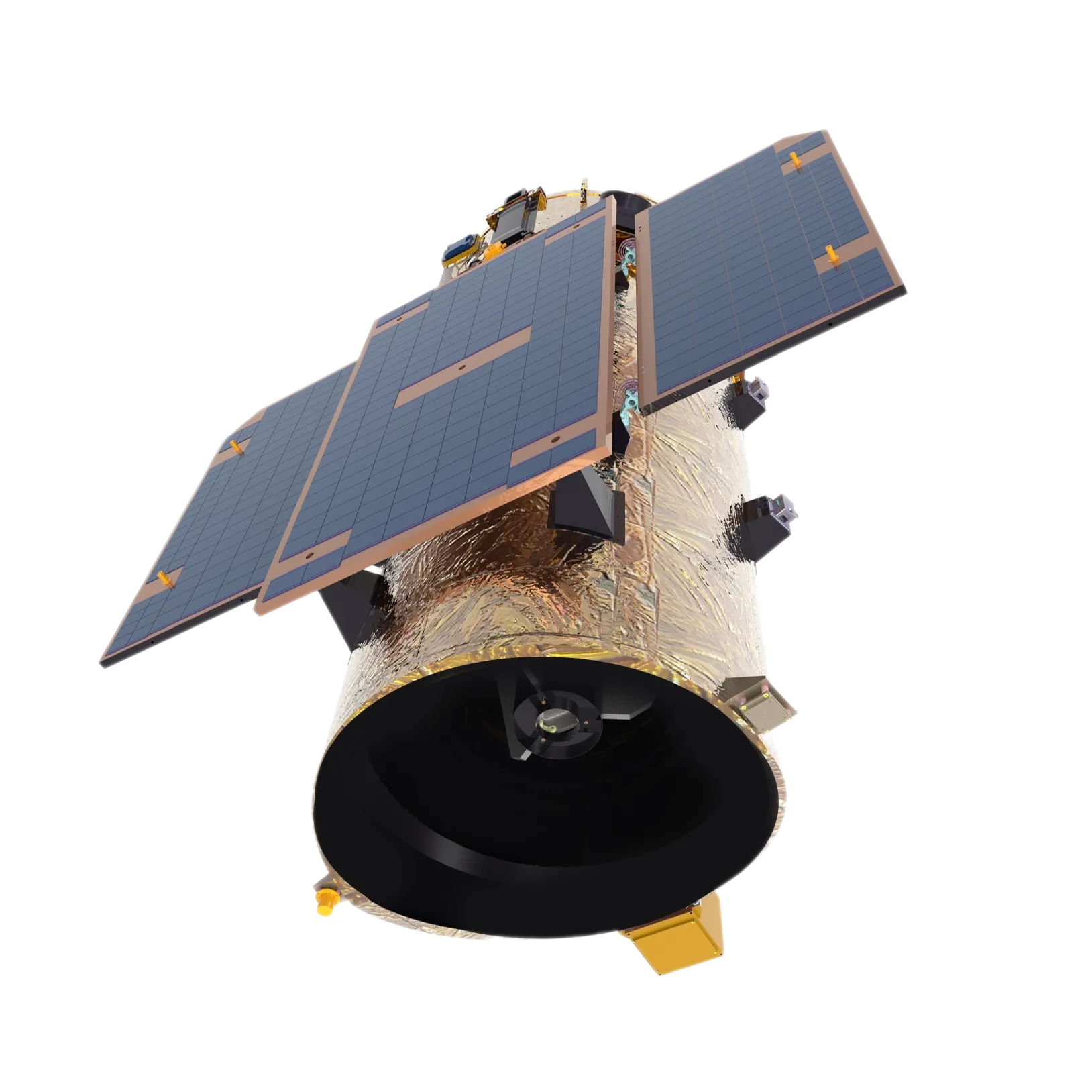
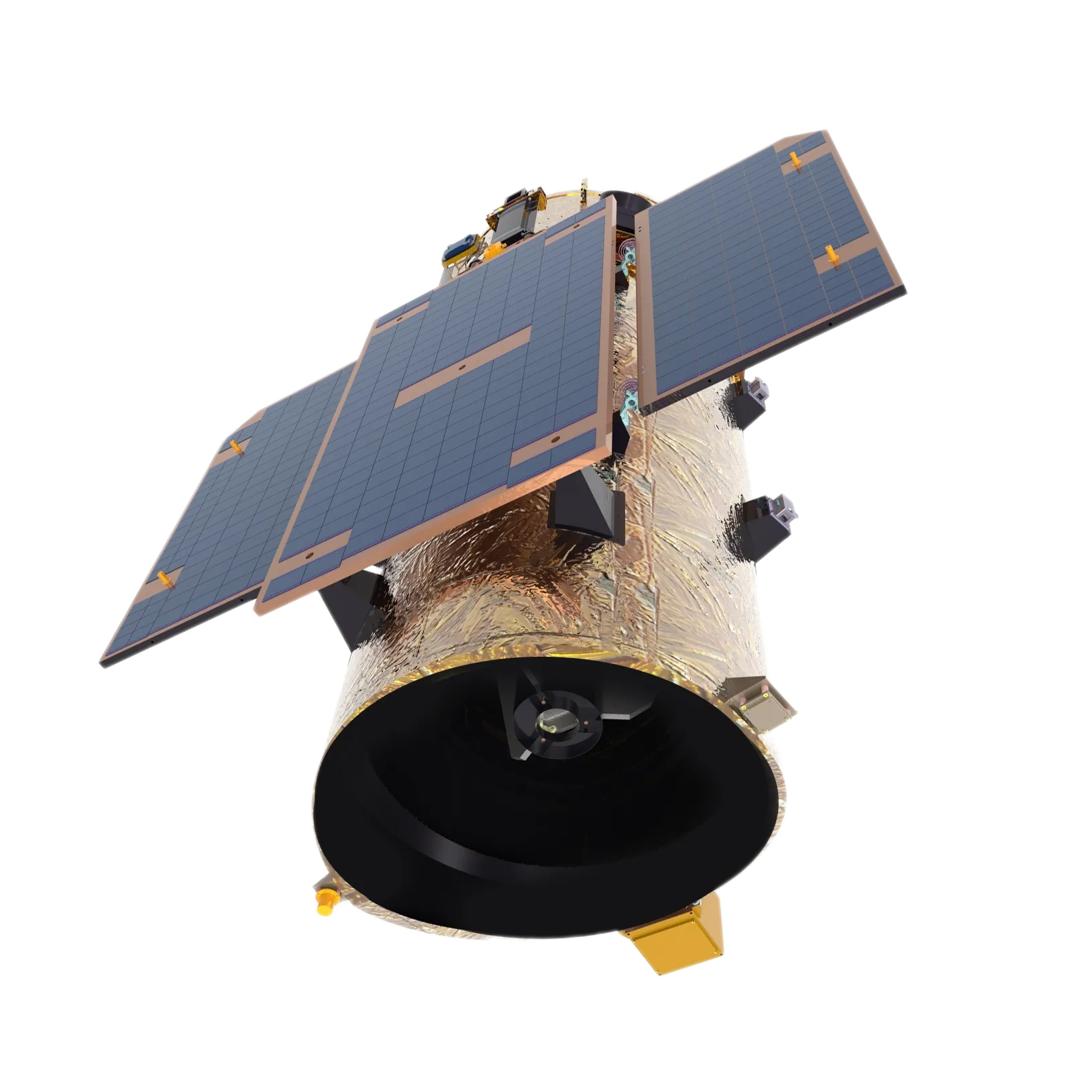
Exploring The Versatility Of Multispectral Camera Technology
In the rapidly evolving field of imaging technology, the multispectral kamẹra stands out as a powerful tool for capturing data beyond the capabilities of conventional cameras. Unlike standard cameras that capture images in the visible spectrum, a multispectral imaging camera collects information across multiple wavelengths, including visible, infrared, and sometimes ultraviolet. This enhanced capability enables applications in agriculture, environmental monitoring, medical diagnostics, and industrial inspection. With advancements in technology, a low cost multispectral camera is increasingly accessible, offering affordable solutions without compromising on functionality. Whether you are looking to ra a multispectral kamẹra or explore lenses tailored for specific spectral needs, understanding the features and uses of this technology can help you leverage its full potential.

Advantages of a Multispectral Imaging Camera
A key feature of any multispectral imaging camera is its ability to capture data in several discrete spectral bands, allowing for detailed analysis of materials and environments. For example, in agriculture, these cameras can detect plant health by measuring reflectance in near-infrared and visible bands, something traditional cameras cannot achieve. This makes multispectral visible imaging cameras especially valuable for precision farming, helping farmers optimize irrigation and fertilization practices. Additionally, the integration of multispectrum infrared combination cameras enhances this capability by allowing simultaneous capture of infrared and visible spectra, providing even richer datasets for analysis.
Choosing the Right Multispectral Lens
The effectiveness of a multispectral kamẹra largely depends on the quality of its lens. A specialized multispectral lens is designed to transmit and focus multiple wavelengths of light accurately onto the sensor without distortion or loss. This ensures that the data captured in different spectral bands remains precise and reliable. When selecting a multispectral lens, considerations include the spectral range it supports, its optical clarity, and compatibility with your camera system. Proper lens selection can enhance image quality and expand the potential applications of your multispectral imaging camera, whether for research, industrial inspection, or environmental monitoring.
Applications and Buying Considerations for Multispectral Cameras
If you plan to ra a multispectral kamẹra, it is essential to consider the intended application to choose the appropriate model. For instance, a low cost multispectral camera may suit educational purposes or preliminary fieldwork, while advanced research might require higher-end models with broader spectral range and better resolution. Many manufacturers offer multispectral visible imaging cameras tailored for specific industries such as forestry, geology, or biomedical fields. Additionally, some cameras combine multispectral and infrared imaging capabilities, often referred to as multispectrum infrared combination cameras, to provide comprehensive data sets. Always evaluate factors such as spectral bands, sensor resolution, compatibility with software, and the availability of suitable multispectral lenses when making your selection.
In conclusion, the multispectral kamẹra technology opens new doors for imaging applications across various fields by capturing data beyond the visible spectrum. The availability of low cost multispectral cameras and specialized lenses makes this technology more accessible, enabling detailed analysis in agriculture, environmental science, and industrial inspection. Whether you are seeking a simple multispectral imaging camera or a sophisticated multispectrum infurarẹẹdi apapo kamẹra, understanding the core features and applications will guide you in making an informed purchase. By integrating this technology into your projects, you can unlock insights that traditional cameras simply cannot provide.