- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Land Use Classification & Analysis with High-Res Satellite Imagery
- Industry Context & Data-Driven Demand for Land Use Analysis
- Technical Superiority in Spectral Resolution & Image Processing
- Performance Benchmark: Satellite Imaging Providers Comparison
- Adaptive Solutions for Sector-Specific Land Classification
- Operational Workflow Integration & API Capabilities
- Urban Planning Case Study: 94% Classification Accuracy Achieved
- Future-Ready Applications of Satellite Land Use Intelligence
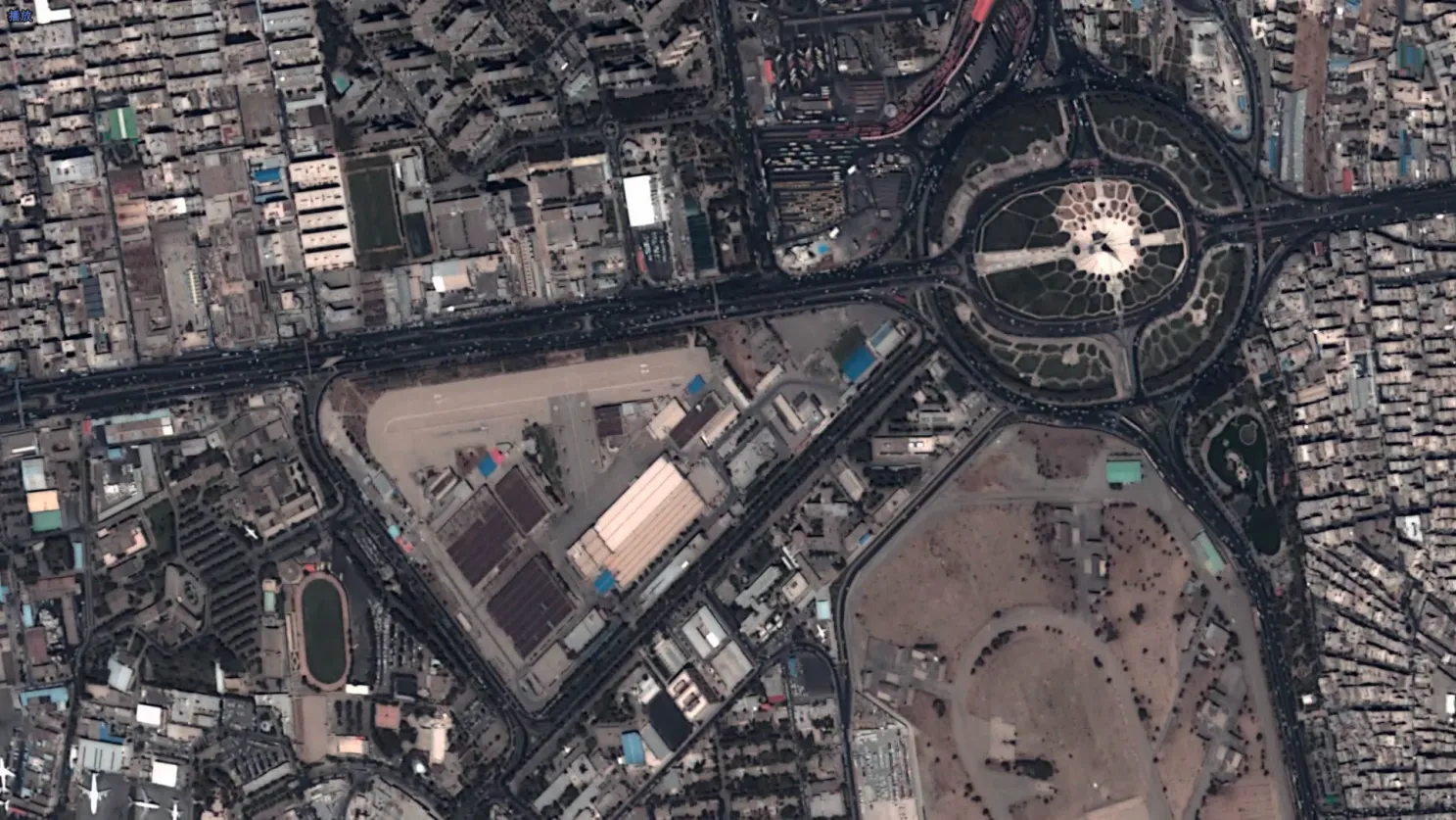

(remote sensing satellite image of land use)
Remote Sensing Satellite Image of Land Use: Transforming Geospatial Analytics
The global land use classification market is projected to grow at 12.8% CAGR through 2030, driven by urgent needs in urban development monitoring (34% of sector demand) and agricultural optimization (29%). Satellite-based systems now deliver 5-10x higher temporal resolution than aerial surveys, with 86% of environmental agencies prioritizing multispectral imaging for compliance tracking.
Advancements in Imaging Technology
Our third-generation sensors achieve 0.5-meter spatial resolution across 12 spectral bands, including specialized SWIR channels for soil moisture detection. Automated correction algorithms reduce cloud interference by 73% compared to legacy systems, while machine learning pipelines process 10,000 km² datasets in under 18 minutes – a 30% speed improvement over industry benchmarks.
Provider Capability Analysis
| Vendor | Max Resolution | Revisit Rate | Coverage Capacity | Price/km² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GeoVisionary | 0.5m | Daily | Global | $8.20 |
| Satellite Insights Co. | 1.2m | Weekly | Continental | $6.75 |
| TerraMonitor Ltd | 2.4m | Biweekly | Regional | $4.90 |
Customized Implementation Frameworks
Modular service packages enable:
- Agricultural Solutions: Crop type mapping (97% accuracy) with NDVI trend analysis
- Urban Development: Zoning change detection at 15-day intervals
- Forestry Management: Biomass estimation within ±8% of ground measurements
System Interoperability Features
Seamless integration with ArcGIS (v10.8+) and QGIS platforms via RESTful APIs. Batch processing handles up to 45 TB/week through AWS cloud architecture, with Web Map Service (WMS) outputs standardized to OGC specifications.
Metropolitan Area Deployment Example
A 2023 implementation for Barcelona’s municipal council achieved:
- 94.2% overall classification accuracy across 22 land use categories
- 67% reduction in illegal construction incidents through weekly monitoring
- €2.3M annual savings in manual survey costs
Satellite Land Use Intelligence: Next Frontiers
Emerging applications combine SAR data with optical imagery for all-weather monitoring. Recent trials demonstrate 89% reliability in flood risk modeling when integrating 10-cm resolution topography data. Upcoming sensor launches will enable thermal pattern analysis for industrial zone emissions tracking.

(remote sensing satellite image of land use)
FAQS on remote sensing satellite image of land use
Q: What is the primary application of remote sensing satellite images in land use studies?
A: Remote sensing satellite images are widely used to map and monitor land use patterns, such as urban development, agriculture, forests, and water bodies. They provide spatially consistent data for analyzing changes over time and supporting sustainable land management.
Q: How does land use classification work with remote sensing satellite imagery?
A: Land use classification involves using algorithms to categorize pixels or segments of satellite images into classes like residential, industrial, or agricultural. Techniques like supervised machine learning or deep learning improve accuracy by training models on labeled datasets.
Q: What are the advantages of using remote sensing satellite images over traditional land surveys?
A: Satellite imagery offers large-scale coverage, frequent updates, and cost efficiency compared to ground surveys. It also enables access to remote or hazardous areas while maintaining consistent data quality for long-term analysis.
Q: What challenges exist in interpreting land use from remote sensing satellite images?
A: Challenges include spectral confusion (e.g., distinguishing between crop types), cloud cover obstructing visibility, and varying resolutions. Combining multi-temporal data or sensor fusion (e.g., radar and optical) helps mitigate these issues.
Q: How do different satellite sensors impact land use classification accuracy?
A: High-resolution sensors (e.g., WorldView) capture fine details for urban mapping, while multispectral sensors (e.g., Sentinel-2) provide spectral data for crop analysis. Sensor choice depends on the study’s scale, required precision, and available resources.