- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
High-Performance Transmission Antenna for Microstrip and Dual Band Needs
In the era of rapid technological development and wireless connectivity, the foundation of efficient data transmission lies in robust transmission antenna solutions. This article delves into the evolving world of transmission antenna technologies, with a special focus on microstrip antenna, circular microstrip antenna, and dual band microstrip patch antenna architectures. We'll explore key industry trends, critical technical parameters, and their expanding applications across diverse sectors.
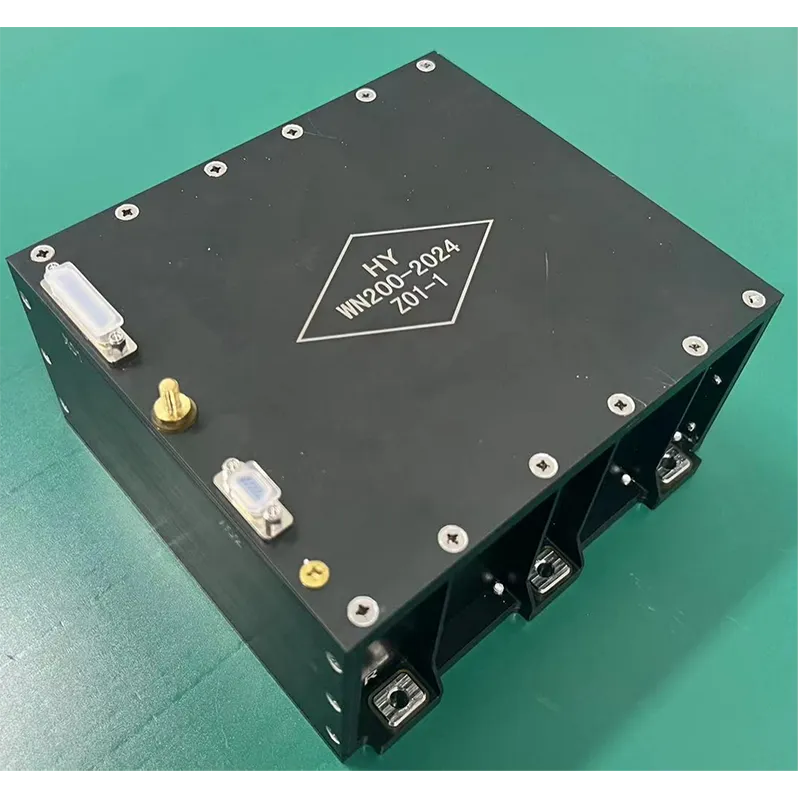
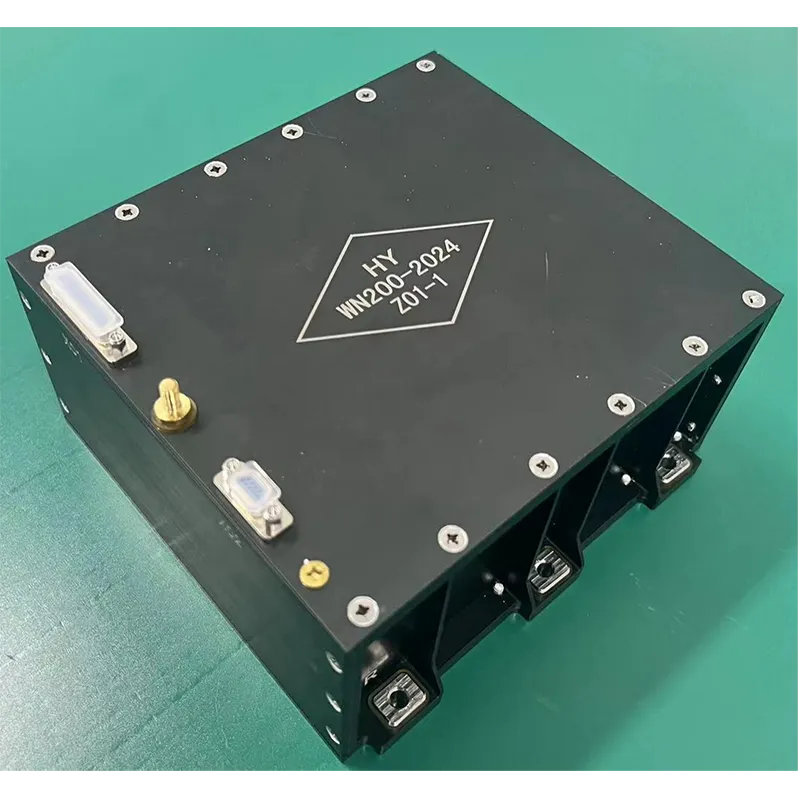
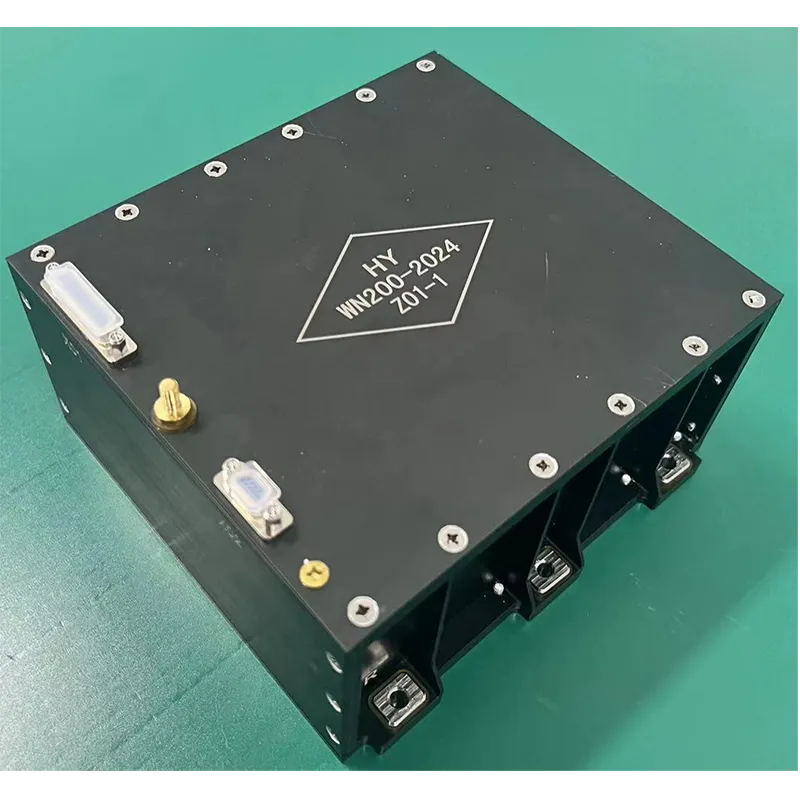
As a leading contributor, SpaceNavi Co.,Ltd. (Official Website) offers state-of-the-art Antenna Products tailored for high-reliability and performance-driven scenarios. Drawing upon peer-reviewed sources and authoritative forums, this article also integrates data visualization to demonstrate the real-world evolution and technical benchmarks of transmission antenna products.
📞: +8613943095588
📱: +86 13943095588
✉: jl1sales02@space-navi.com
🏢: No. 1299 Mingxi Road, Beihu Science and Technology Development Zone, Changchun, Jilin Province.
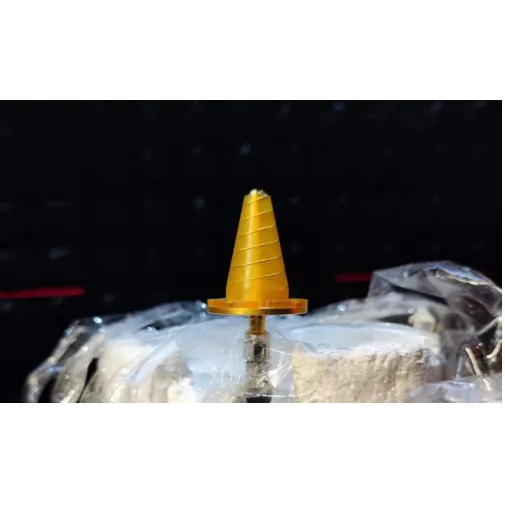

The world of transmission antenna systems is characterized by exponential growth in data, IoT, and wireless communications. According to research from IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, the evolution from traditional dipole to microstrip and phased-array antennas has resulted in shrinking form factors and higher integration capabilities.
- Increasing demand for dual band microstrip patch antennas in 5G/IoT applications.
- Proliferation of circular microstrip antenna in satellite and aerospace industries for polarization diversity and compact size [ScienceDirect].
- Focus on materials science: use of advanced substrates (e.g., Rogers, Teflon-based), low-loss dielectrics, and conformal antenna design.
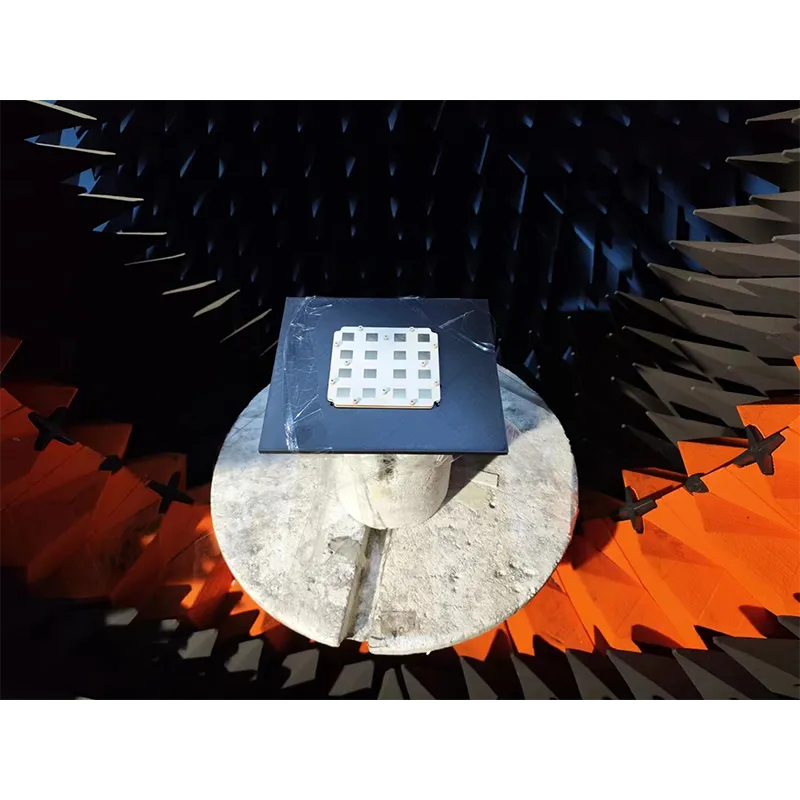
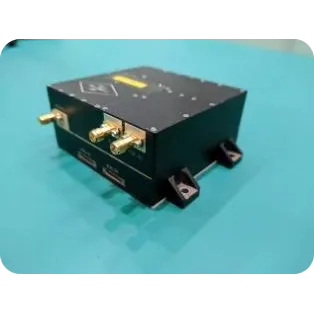
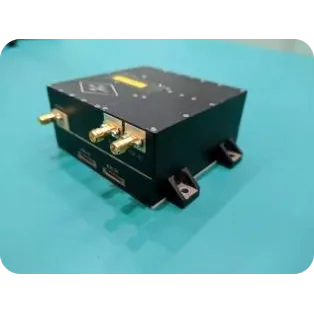
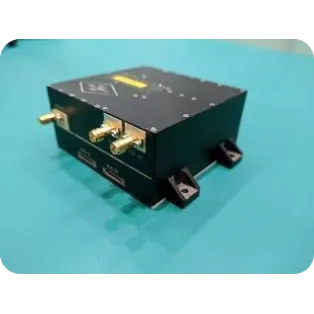
SpaceNavi Co.,Ltd.'s transmission antenna solutions are engineered to address these technological shifts, offering versatility across commercial, defense, automotive, satellite, and industrial sectors.
| Parameter | Microstrip Antenna | Circular Microstrip Antenna | Dual Band Microstrip Patch Antenna |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 1 GHz - 40 GHz | 2 GHz - 30 GHz | 2.4/5.2 GHz, 1800/2600 MHz, etc. |
| Gain (dBi) | 4 - 8 | 5 - 9 | 6 - 11 |
| VSWR | < 2:1 | < 1.7:1 | < 1.5:1 |
| Polarization | Linear/CP | Circular | Linear/CP/DP |
| Size (mm) | 15 × 15 to 100 × 100 | Diameter: 25 - 80 | Varies (often compact) |
| Bandwidth | 2% - 15% | 3% - 10% | 5% - 18% |
| Substrate | FR4, Rogers, Teflon | Rogers, Taconic | Rogers, Teflon, Custom |
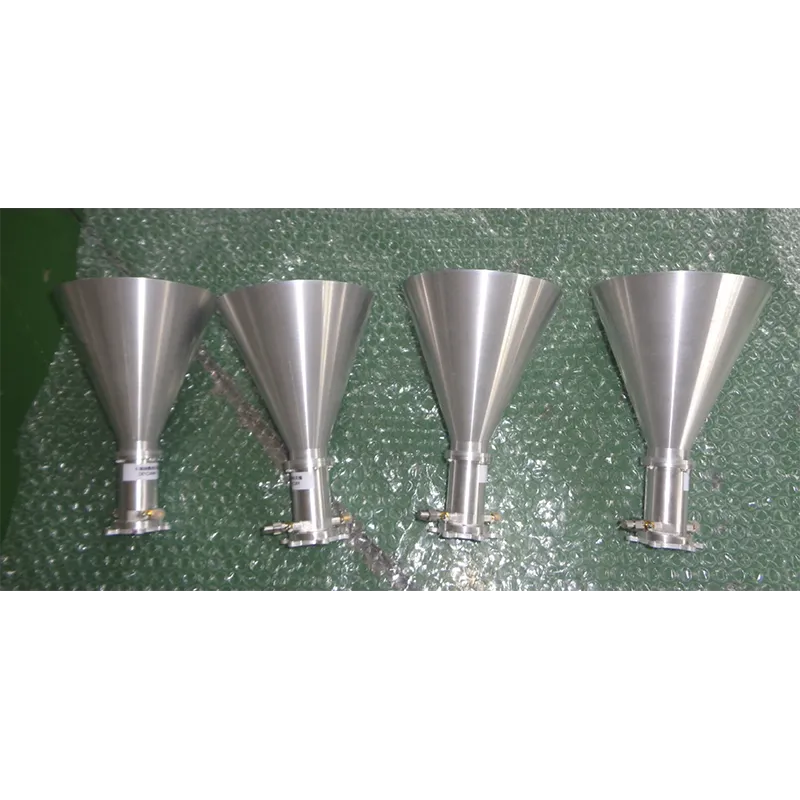


Visualizing the technical evolution of transmission antenna products helps customers and engineers make data-driven decisions on technology adoption.
— Source: All About Circuits Forum - Antenna Theory
SpaceNavi Co.,Ltd. develops comprehensive transmission antenna (Antenna Products) portfolio meeting harsh requirements of modern wireless infrastructure. This includes microstrip antennas, circular microstrip antennas, and dual band microstrip patch antennas. The designs are meticulously engineered for:
- Optimized bandwidth efficiency for next-gen IoT/5G/LTE systems.
- Robust polarization characteristics for satellite and aerospace communication.
- Compact footprint, enabling seamless integration into PCB and high-density electronic applications.
- Strict adherence to ISO9001, CE, and RoHS certification standards for global applications.
- Support for custom frequency bands and special substrate materials per project needs.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure: Macro, pico, and femto cell deployments for 4G/5G.
- Satellite & Aerospace Engineering: Precision navigation, telemetry, Earth observation, and satellite internet.
- Internet of Things (IoT) & Smart Cities: Sensor networks, asset tracking, intelligent transportation, and public safety.
- Automotive & Transportation: V2X communication, autonomous vehicle navigation, and infotainment.
- Military & Defense: Secure communication, radar and electronic countermeasures, as referenced by NI White Paper.
- Industrial & Medical: Industrial wireless automation, wireless medical telemetry and imaging.
As highlighted by discussions on All About Circuits Forum and detailed in IEEE scholarly publications, the design and manufacture of transmission antenna require a deep multidisciplinary understanding of electromagnetic theory, materials science, and international certification protocols.
SpaceNavi Co.,Ltd. demonstrates these principles through:
- Experienced research and engineering team dedicated to innovation in microstrip, circular, and dual band antenna topologies.
- Compliance with global industry standards (ISO9001, ETSI, CE).
- Customization and technical support, ensuring customer projects achieve optimal RF performance.
With exponential advances in wireless system design, the role of the transmission antenna extends far beyond signal propagation—it is strategic for network efficiency, device miniaturization, and future-proofing connectivity infrastructure. Firms such as SpaceNavi Co.,Ltd. lead the charge by combining specialized design, cutting-edge materials, and precision manufacturing in their Antenna Products.
- “Recent Advances in Microstrip Antenna Technology”, IEEE Xplore
- “Circular Microstrip Patch Antenna for Satellite Communications”, ScienceDirect
- “Antenna Selection for Radar and Communications Systems”, NI White Paper
- Community discussion on antenna trends: All About Circuits Forum
This is the first article