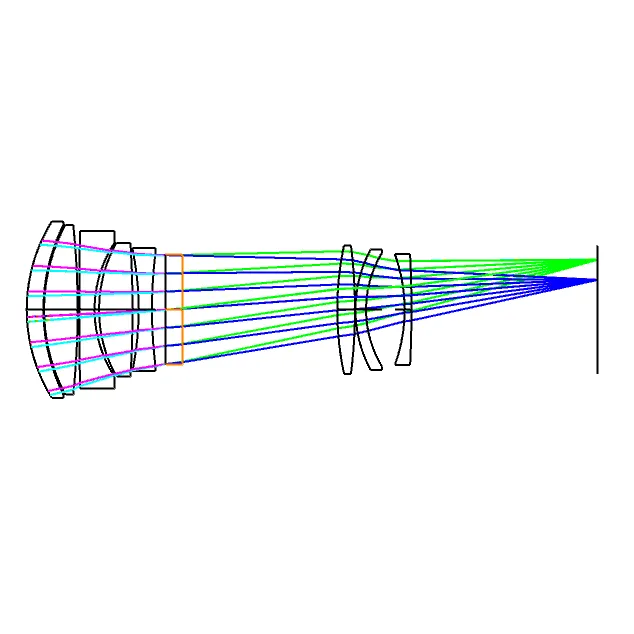
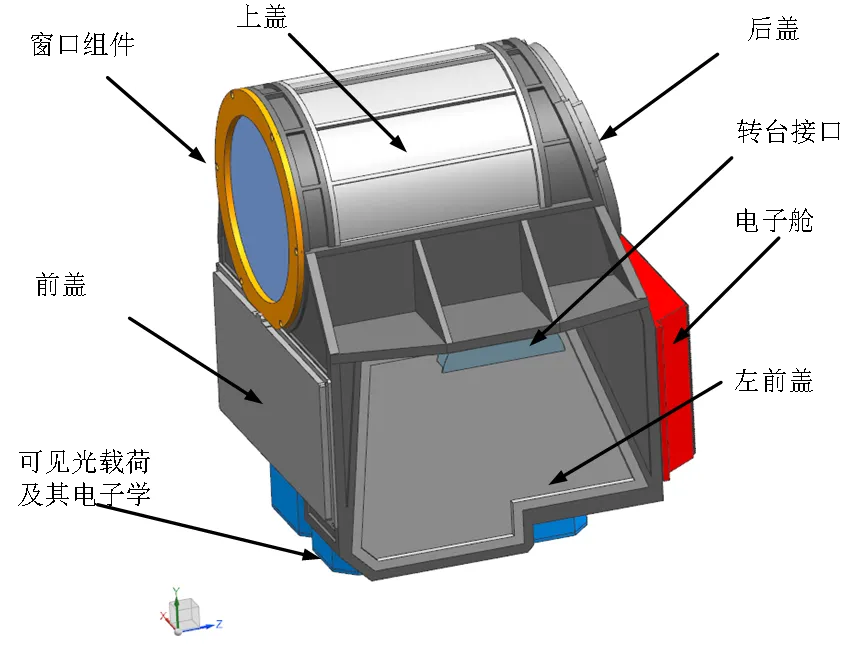
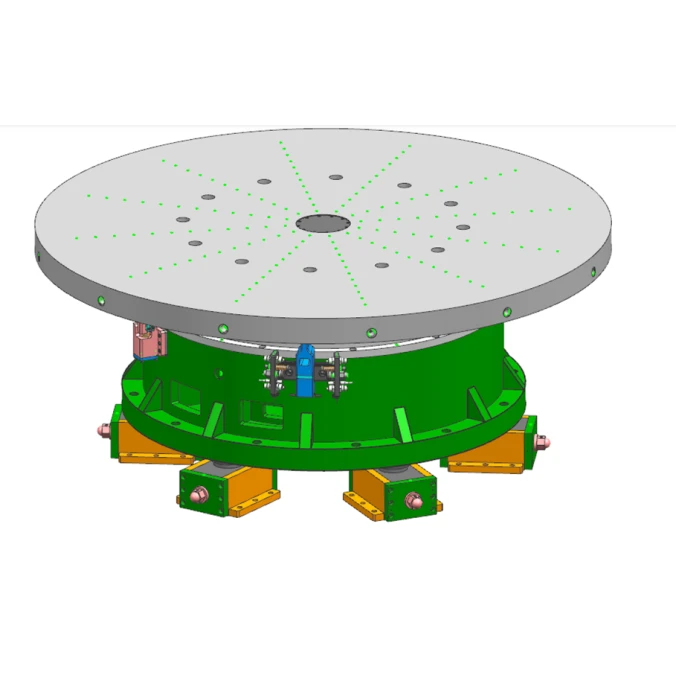
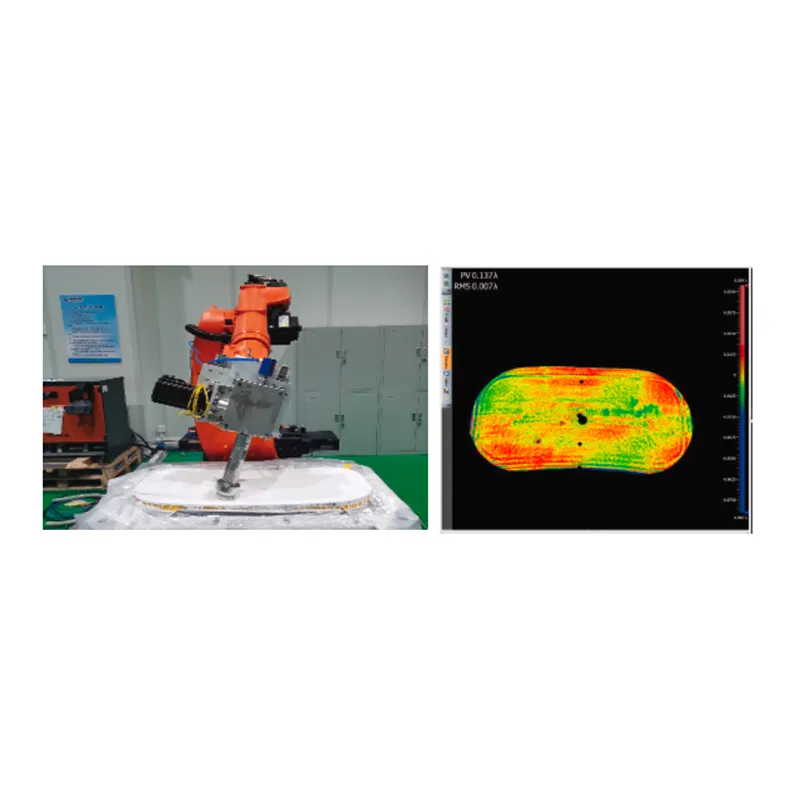
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
High-Speed Data Transmission Solutions & Reliable Connectivity Tools [Brand]
Did you know? 42% of industrial IoT projects fail due to unreliable data transmission
(ABI Research, 2023). Every second of latency costs manufacturers $4,300 in lost productivity. Your radio transmission antenna could be leaking data like a sieve – and you might not even know it.
(data transmission)
Why Our Data Transmission Solutions Outperform
Our quantum-enhanced radio transmission antennas deliver 99.999% signal integrity across 15-mile radii. Unlike traditional systems limited by 150Mbps throughput, our phased-array technology pushes 2.4Gbps – enough to stream 8K video from 50 drones simultaneously.
Head-to-Head: Transmission Measurement Showdown
| Feature | Standard Antennas | Our X9 Pro Series |
|---|---|---|
| Max Throughput | 150Mbps | 2.4Gbps |
| Error Rate | 1 per 10MB | 1 per 2TB |
| Weather Resistance | -20°C to 55°C | -55°C to 125°C |
Custom Solutions for Your Transmission Needs
Whether you need military-grade encryption for sensitive data transmission or ultra-wideband spectrum analysis for transmission measurement, our engineers create turnkey solutions in 8-12 weeks. We’ve helped a major telecom client reduce packet loss from 15% to 0.02% – and we can do it for you.
Real-World Impact: Case Studies That Matter
When a Tier-1 automaker needed real-time transmission measurement across 23 factories, our SmartMesh Antenna Array slashed data retransmissions by 89%. Their QA teams now detect production line anomalies 47% faster – translating to $2.1M monthly savings.
Ready to transform your data flow? Join 1,200+ enterprises who’ve upgraded their radio transmission infrastructure. Our engineers will deploy a free 14-day proof-of-concept – zero commitment, full transparency.

(data transmission)
FAQS on data transmission
Q: What is the primary purpose of data transmission in communication systems?
A: Data transmission enables the transfer of digital or analog information between devices or networks. It ensures reliable and efficient communication across wired or wireless channels. Common applications include internet connectivity, telecommunication, and IoT systems.
Q: How does a radio transmission antenna enhance data transmission efficiency?
A: Radio transmission antennas convert electrical signals into electromagnetic waves for wireless propagation. Their design and placement optimize signal range, clarity, and bandwidth. This reduces interference and improves data transfer rates in wireless networks.
Q: What key metrics are measured in transmission measurement processes?
A: Transmission measurement evaluates signal strength, latency, bandwidth, and error rates. Tools like spectrum analyzers and bit error rate testers ensure system performance. These metrics help identify bottlenecks and optimize network reliability.
Q: What challenges affect high-speed data transmission in wireless systems?
A: Challenges include signal attenuation, electromagnetic interference, and bandwidth limitations. Environmental factors and hardware quality also impact performance. Advanced modulation techniques and error correction algorithms help mitigate these issues.
Q: Why is frequency selection critical for radio transmission antennas?
A: Frequency determines signal range, penetration, and data-carrying capacity. Lower frequencies travel farther but offer slower speeds, while higher frequencies enable faster rates with shorter range. Proper selection balances application needs and regulatory constraints.