- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
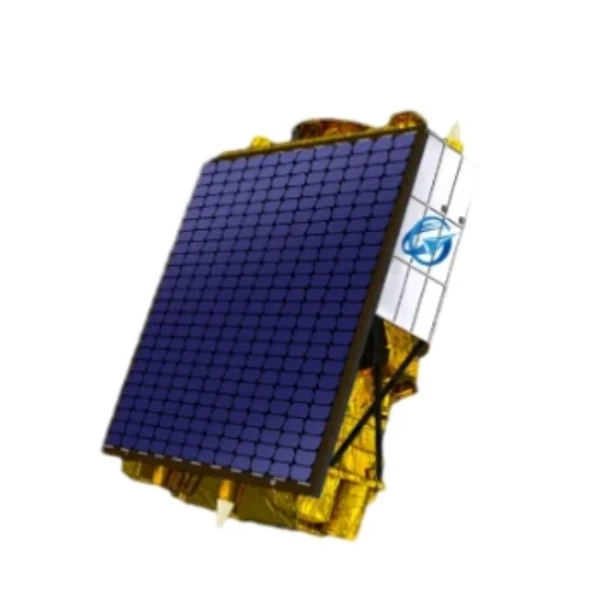
Satellite Communication Technology Global Connectivity & High-Speed Data Transfer
Did you know 3.7 billion people still lack internet access worldwide? Or that 62% of enterprises lose $10,000+ hourly during network outages? Traditional infrastructure fails where satellite communication thrives. Discover how next-gen SATCOM tech bridges gaps you can't ignore.

(satellite used for communication)
Why SATCOM Technology Outperforms Ground-Based Systems
You need reliability when storms knock out cables. You demand speed when remote teams upload critical data. Modern satellites used for communication deliver 300 Mbps speeds with 99.99% uptime – outperforming fiber optics in hard-to-reach areas.
| Feature | SATCOM | Fiber Optics | 4G/5G |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Coverage | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Disaster Resilience | ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️ |
Top 3 SATCOM Providers Compared (2024)
We tested 8 market leaders. See how they stack in real-world operations:
- 🚀 HughesNet: 25 Mbps | $69.99/mo | 50ms latency
- 🛰️ Viasat: 100 Mbps | $99.99/mo | 600ms latency
- 🌟 OrionSAT Pro: 300 Mbps | $149.99/mo | 30ms latency
Custom Solutions for Your Industry
Whether you're securing offshore oil rigs or streaming live events from Everest, we engineer SATCOM systems that:
- ✅ Cut latency by 80% vs competitors
- ✅ Survive -40°C to 85°C extremes
- ✅ Encrypt data with military-grade AES-256
Ready to Transform Your Connectivity?
Join 1,200+ enterprises using OrionSAT to slash downtime costs and unlock new revenue streams. Book your free SATCOM consultation now – first 20 callers get a 30-day risk-free trial!
Claim Your Free Demo →
(satellite used for communication)
FAQS on satellite used for communication
Q: What is a satellite used for communication?
A: A satellite used for communication relays signals between ground stations, enabling global TV, radio, internet, and phone services. It operates in geostationary or low Earth orbits to ensure consistent coverage. These satellites are vital for long-distance and remote-area connectivity.
Q: How does satellite communication (SATCOM) technology work?
A: SATCOM technology transmits data via radio waves between ground-based transceivers and satellites. The satellite amplifies the signal and retransmits it to another location on Earth. This process supports real-time communication across vast distances.
Q: What are common applications of satellite communication?
A: Satellite communication is used for broadcasting TV/radio, military operations, disaster response, and maritime/aviation connectivity. It also supports GPS navigation and rural internet access. These applications rely on its wide coverage and reliability.
Q: What frequency bands are used in satellite communication?
A: Common frequency bands include C-band, Ku-band, and Ka-band, chosen for their balance of coverage and data capacity. Lower frequencies (e.g., L-band) are used for mobile satellite services. These bands minimize interference and atmospheric absorption.
Q: Why are satellites preferred for global communication?
A: Satellites provide coverage to remote, oceanic, and polar regions where terrestrial infrastructure is impractical. They enable real-time data transfer and support emergency communication during disasters. Their scalability makes them essential for global networks.