- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Warning: Undefined array key "array_term_id" in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /home/www/wwwroot/HTML/www.exportstart.com/wp-content/themes/1371/header-lBanner.php on line 78
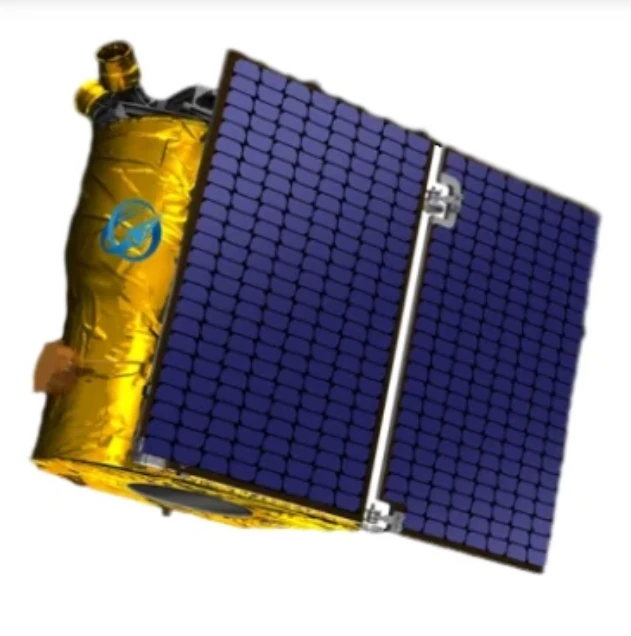
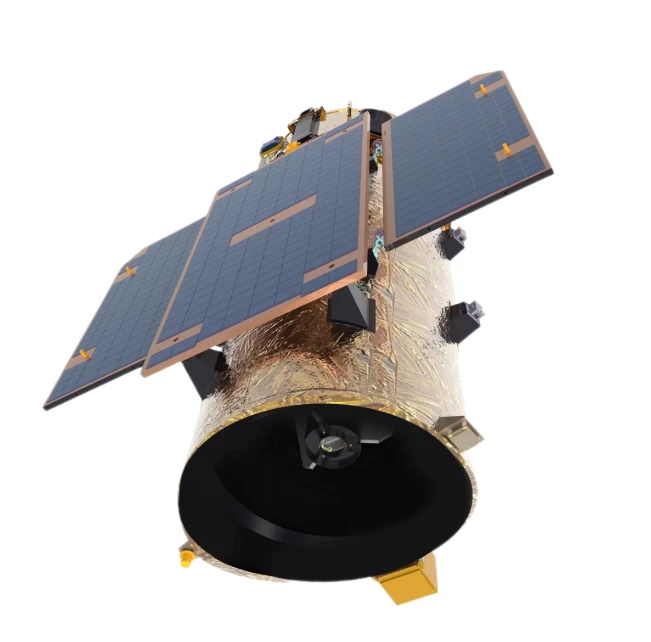
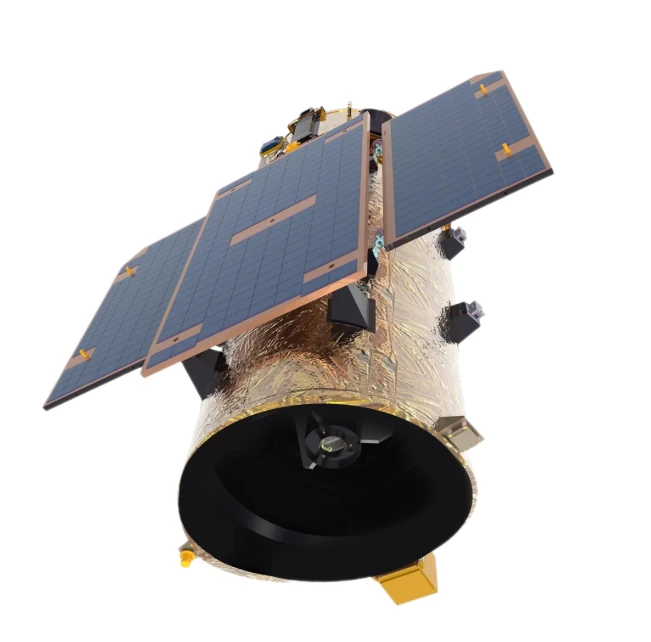
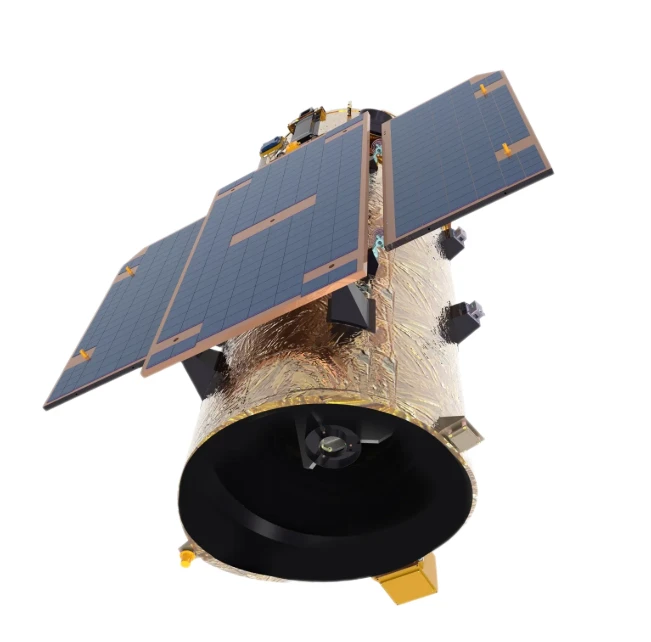
LEO Satellite Network High-Speed, Low-Latency Global Connectivity
Did you know 3.7 billion people still lack reliable internet access? Traditional GEO satellites struggle with latency over 600ms, while LEO satellite technology delivers speeds under 50ms. This isn’t just an upgrade—it’s a game-changer for remote businesses, emergency response teams, and global IoT deployments.

(leo satellite network)
Technical Superiority: How LEO Satellite Networks Outperform GEO
LEO satellites orbit 1,200km above Earth—20x closer than GEO systems. This proximity means:
- ✅ 25-50ms latency vs. 600ms+ in GEO
- ✅ 95% global coverage with 1,000+ satellites
- ✅ 300Mbps+ download speeds for enterprise users
Head-to-Head: LEO vs. GEO Satellite Systems
Custom Solutions for Enterprise Needs
Our modular LEO systems offer:
Maritime Package
✔️ 99.9% uptime guarantee
✔️ 50Mbps minimum speed
✔️ Real-time weather analytics
Real-World Success: Mining Operation Case Study
A Siberian mining company reduced communication costs by 60% using our LEO network. They achieved:
- 📈 45% faster data transmission
- 🛡️ Military-grade encryption
Ready for the Connectivity Revolution?
Join 500+ enterprises using our LEO satellite network solutions. Book your free consultation today and get 15% off first-year service!
(leo satellite network)
FAQS on leo satellite network
Q: What is a LEO satellite network?
A: A LEO satellite network consists of satellites orbiting Earth at altitudes between 500-2,000 km. These networks provide low-latency communication and global coverage, making them ideal for internet services and real-time data transmission.
Q: How does LEO satellite technology differ from GEO systems?
A: LEO satellites operate closer to Earth, reducing latency to 20-40 ms, while GEO satellites at 35,786 km have higher latency (500+ ms). LEO networks also require constellations of hundreds to thousands of satellites for continuous coverage.
Q: What are the advantages of LEO satellite networks over GEO?
A: LEO networks offer faster data speeds, lower latency, and better polar region coverage. They are more resilient to signal interference and can support emerging technologies like IoT and 5G connectivity.
Q: What challenges do LEO satellite systems face?
A: Challenges include high deployment costs for large constellations, frequent satellite replacements due to shorter orbital lifespans, and complex ground station coordination to manage rapid signal handovers.
Q: Can LEO and GEO satellite systems work together?
A: Yes, hybrid systems combine GEO's wide-area coverage with LEO's low-latency capabilities. This integration optimizes bandwidth allocation and supports diverse applications like emergency communications and military operations.
Q: How do LEO satellites achieve global internet coverage?
A: Through interconnected constellations using inter-satellite links (ISLs), LEO satellites create a mesh network. This allows data to hop between satellites, reducing reliance on ground infrastructure for global connectivity.
Q: Are LEO satellite networks sustainable long-term?
A: Sustainability concerns include space debris management and energy consumption. Companies are developing collision-avoidance systems and reusable rockets to mitigate environmental and operational risks.