- africano
- albanés
- Amárico
- árabe
- armenio
- Azerbaiyano
- vasco
- Bielorruso
- bengalí
- bosnio
- búlgaro
- catalán
- Cebuano
- Porcelana
- corso
- croata
- checo
- danés
- Holandés
- Inglés
- esperanto
- Estonio
- finlandés
- Francés
- frisio
- gallego
- georgiano
- Alemán
- Griego
- Gujarati
- Criollo haitiano
- Hausa
- hawaiano
- hebreo
- No
- Miao
- húngaro
- islandés
- igbo
- indonesio
- irlandés
- italiano
- japonés
- javanés
- Canarés
- kazajo
- Jemer
- Ruanda
- coreano
- kurdo
- Kirguistán
- Mano de obra
- latín
- letón
- lituano
- Luxemburgués
- macedónio
- madagascarí
- malayo
- Malabar
- maltés
- maorí
- Maratí
- mongol
- Birmania
- Nepalí
- noruego
- noruego
- Occitano
- Pashto
- persa
- Polaco
- portugués
- punjabi
- rumano
- ruso
- Samoano
- Gaélico escocés
- serbio
- Inglés
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Cingalés
- eslovaco
- esloveno
- somalí
- Español
- Sundanés
- swahili
- sueco
- Tagalo
- Tayiko
- Tamil
- Tártaro
- Télugu
- tailandés
- turco
- Turcomano
- ucranio
- Urdú
- Uigur
- Uzbeko
- vietnamita
- galés
- Ayuda
- yídish
- Yoruba
- zulú
Enhancing Agricultural Monitoring with Multispectral Camera Technology
In the age of precision agriculture and environmental stewardship, the cámara multiespectral has become a cornerstone of intelligent monitoring systems. With its ability to capture data across multiple light bands, this advanced optical tool helps identify plant health, soil conditions, and environmental changes in real time.
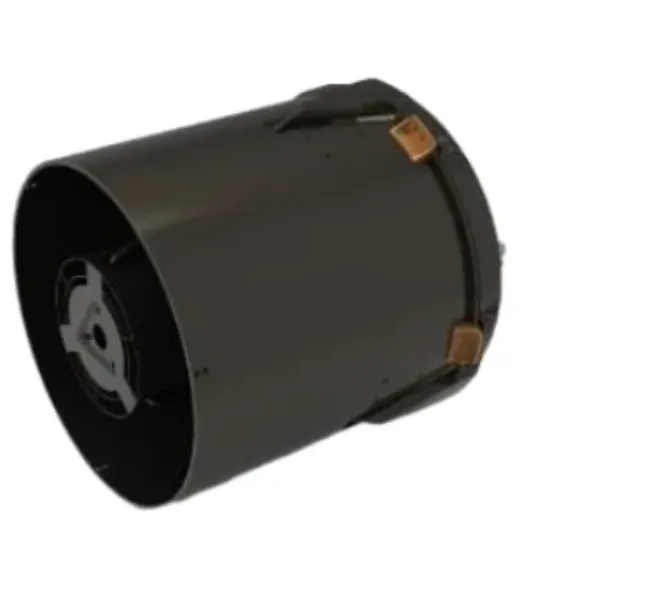

From drone integrations to fixed installations, today’s multispectral imaging camera technology is transforming how we observe and respond to natural ecosystems.
What Sets a Multispectral Camera Apart?
Unlike standard RGB cameras that only detect visible light, a cámara multiespectral can capture information across a spectrum that includes near-infrared (NIR), red-edge, and ultraviolet. These additional bands provide valuable insights into vegetation indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), which are critical for modern farming.
Whether you're using a multi spectral camera or a high-end multispectral visible imaging camera, the goal is the same: translate invisible data into actionable intelligence.
Low Cost Solutions for Precision Farming
Increased availability of low cost multispectral camera options is making spectral imaging more accessible for farms of all sizes. These affordable models often feature compact sensors and lightweight builds, perfect for mounting on drones for aerial surveys. With these cameras, farmers can quickly evaluate:
Crop stress before visible symptoms appear
Water and nutrient distribution
Pest or disease outbreaks
Soil fertility zones
For those seeking to buy multispectral camera products, many manufacturers now offer plug-and-play systems with pre-set spectral bands and cloud connectivity for rapid data processing.
Hybrid Technologies and Spectral Fusion
Advanced systems, like the cámara combinada infrarroja multiespectro, offer an integrated approach that merges multispectral data with thermal imaging. This fusion enhances detection capabilities in challenging conditions such as cloudy weather or dusk operations. The result: clearer visuals of canopy structure, soil temperature, and moisture gradients.
In this segment, multispectral lens technology plays a pivotal role. These precision lenses focus multiple wavelengths onto sensitive sensor arrays, ensuring accuracy even in dynamic environments.
Environmental Applications Beyond Farming
Beyond agriculture, the cámara multiespectral is increasingly used in environmental monitoring. Conservationists and researchers deploy these cameras to:
Track deforestation
Monitor algae blooms in water bodies
Assess wildfire risk areas
Observe glacier or wetland health
The rising interest in multispectral camera price transparency reflects the growing market for this technology in government, NGO, and research sectors. The affordability and portability of newer models enable real-time data collection in remote or sensitive areas, often using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Buying and Deploying the Right System
Choosing the right cámara multiespectral involves evaluating parameters like spatial resolution, number of spectral bands, frame rate, and integration compatibility. For instance, if you're focusing on drone-based crop scanning, selecting a lightweight low cost multispectral camera with five-band coverage (Blue, Green, Red, Red-edge, NIR) is typically sufficient.
Suppliers offer guidance and software support to help users interpret and apply collected data. For example, when you buy multispectral camera, it often comes with NDVI calculation tools and real-time display options.
The cámara multiespectral is more than just an imaging device—it's a decision-making assistant for smarter agriculture and environmental care. Whether you're exploring a multispectral camera buy for your UAV system or researching the optimal multispectral camera price, these technologies promise high return on investment by improving resource efficiency and early problem detection.
As innovation continues, the future of multispectral imaging camera systems will involve greater resolution, cloud-based analytics, and seamless multisensor integration—paving the way for more sustainable farming and ecosystem management.