- አፍሪካዊ
- አልበንያኛ
- አማርኛ
- አረብኛ
- አርመንያኛ
- አዘርባጃኒ
- ባስክ
- ቤላሩሲያን
- ቤንጋሊ
- ቦስንያን
- ቡልጋርያኛ
- ካታሊያን
- ሴቡአኖ
- ቻይና
- ኮርሲካን
- ክሮኤሽያን
- ቼክ
- ዳኒሽ
- ደች
- እንግሊዝኛ
- እስፔራንቶ
- ኢስቶኒያን
- ፊኒሽ
- ፈረንሳይኛ
- ፍሪሲያን
- ጋላሺያን
- ጆርጅያን
- ጀርመንኛ
- ግሪክኛ
- ጉጅራቲ
- ሓይቲያን ክሬኦሌ
- ሃውሳ
- ሐዋያን
- ሂብሩ
- አይ
- ሚያኦ
- ሃንጋሪያን
- አይስላንዲ ክ
- igbo
- ኢንዶኔዥያን
- አይሪሽ
- ጣሊያንኛ
- ጃፓንኛ
- ጃቫኒስ
- ካናዳ
- ካዛክሀ
- ክመር
- ሩዋንዳኛ
- ኮሪያኛ
- ኩርዲሽ
- ክይርግያዝ
- የጉልበት ሥራ
- ላቲን
- ላትቪያን
- ሊቱኒያን
- ሉክዜምብርጊሽ
- ማስዶንያን
- ማላጋሲያ
- ማላይ
- ማላያላም
- ማልትስ
- ማኦሪይ
- ማራቲ
- ሞኒጎሊያን
- ማይንማር
- ኔፓሊ
- ኖርወይኛ
- ኖርወይኛ
- ኦሲታን
- ፓሽቶ
- ፐርሽያን
- ፖሊሽ
- ፖርቹጋልኛ
- ፑንጃቢ
- ሮማንያን
- ራሺያኛ
- ሳሞአን
- ስኮትላንዳዊ ጌሊክ
- ሰሪቢያን
- እንግሊዝኛ
- ሾና
- ስንድሂ
- ሲንሃላ
- ስሎቫክ
- ስሎቬንያን
- ሶማሊ
- ስፓንኛ
- ሱዳናዊ
- ስዋሕሊ
- ስዊድንኛ
- ታንጋሎግ
- ታጂክ
- ታሚል
- ታታር
- ተሉጉ
- ታይ
- ቱሪክሽ
- ቱሪክሜን
- ዩክሬንያን
- ኡርዱ
- ኡጉር
- ኡዝቤክ
- ቪትናሜሴ
- ዋልሽ
- እገዛ
- ዪዲሽ
- ዮሩባ
- ዙሉ
Empowering Wireless Systems With 2.4 GHz Microstrip Patch Antenna And Aperture Coupled Designs
As wireless connectivity becomes an integral part of our lives, from smart homes to industrial automation, antenna design has emerged as a key factor in achieving fast, reliable, and efficient communication. Among the various solutions, the 2.4 GHz microstrip patch antenna and aperture coupled microstrip antenna stand out for their compact structure, performance reliability, and adaptability across industries.
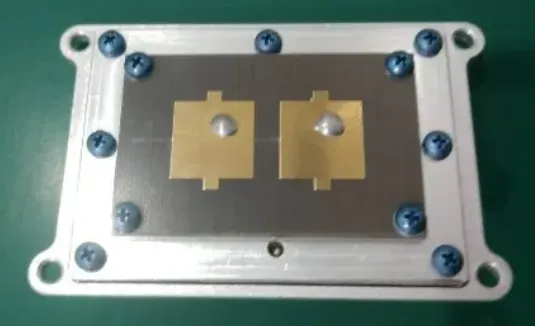
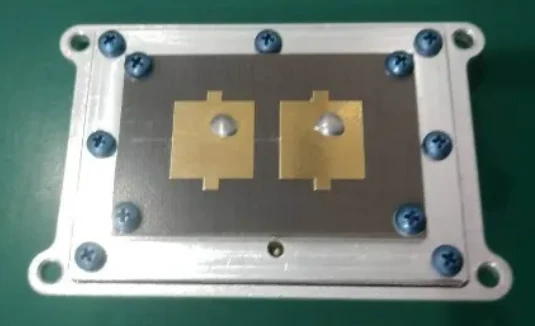
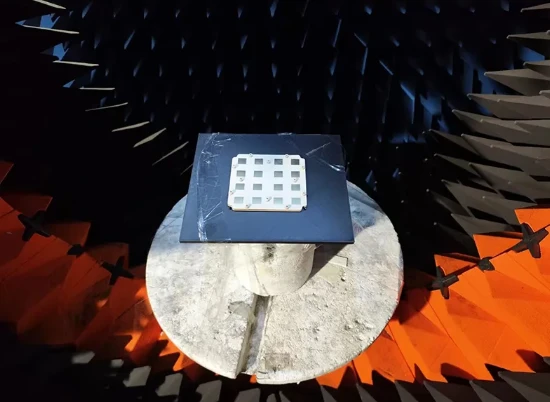
Engineers and manufacturers are increasingly turning to advanced microstrip antenna designs to meet the demands of modern devices, ensuring signal integrity while minimizing weight and space.
2.4 GHz Microstrip Patch Antenna: Compact And Optimized For IoT
The 2.4 GHz microstrip antenna is widely used in applications such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee due to its compatibility with the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, Medical) band. This frequency is globally unlicensed, making it ideal for universal wireless communication.
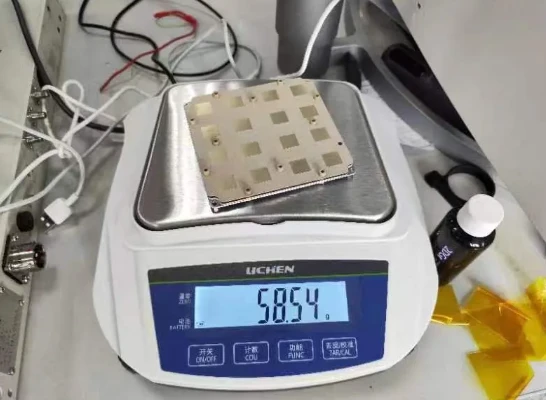
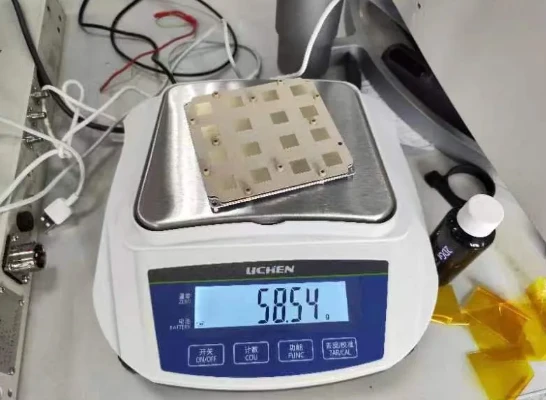
The 2.4 GHz microstrip patch antenna specifically features a low-profile, flat design that makes it perfect for compact devices, such as smart sensors, wearables, and wireless controllers. Its patch design allows easy integration onto PCBs, supporting mass production without sacrificing performance.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, the demand for 2.4 GHz microstrip patch antennas rises—offering designers a reliable solution that combines efficiency with scalability.
Aperture Coupled Microstrip Antenna: Improving Bandwidth And Performance
For applications requiring broader bandwidth and better isolation, the aperture coupled microstrip antenna is an excellent choice. In this design, the radiating patch is fed through a small aperture or slot in the ground plane. This feeding technique reduces surface wave loss and improves impedance matching—resulting in enhanced bandwidth and gain.
Aperture coupled microstrip antennas are commonly found in satellite communications, wireless LANs, radar systems, and aerospace applications. Their flexibility allows designers to adjust aperture size, shape, and substrate properties to tune antenna performance as required.
This innovative structure also allows better decoupling of the radiating element from the feed line, minimizing cross-polarization and signal distortion.
Integrating Microstrip Antennas In Modern Wireless Devices
Whether you're working on short-range communication tools or developing compact telemetry systems, microstrip antenna solutions offer unmatched design versatility. From the traditional microstrip patch antenna to specialized versions like the circular microstrip patch antenna or broadband microstrip antenna, engineers can tailor each design to specific use cases and frequency bands.
For consumer electronics, the 2.4 GHz microstrip antenna remains one of the most reliable options for maintaining stable connections in devices such as routers, drones, wireless headphones, and remote controls.
Meanwhile, innovations like the broadband microstrip patch antenna help future-proof designs by supporting multiband communication—an essential feature for upcoming 5G and hybrid networks.
The rise of wireless technology demands compact, efficient, and high-performance antenna designs. The 2.4 GHz microstrip patch antenna delivers a proven solution for compact IoT and wireless systems, while the aperture coupled microstrip antenna pushes performance boundaries with enhanced bandwidth and signal purity.
Together with versatile configurations like the circular microstrip antenna and broadband microstrip antenna, these technologies empower the next generation of wireless communication across industries—from smart homes to aerospace.
Choosing the right antenna design isn’t just about frequency—it's about maximizing efficiency, minimizing interference, and ensuring seamless integration into your final product.