- afrikalik
- alban
- Amhar
- arabcha
- arman
- ozarbayjon
- bask
- belarus
- bengal
- bosniyalik
- bolgar
- katalan
- Sebuano
- Xitoy
- Korsika
- xorvat
- chex
- Daniya
- golland
- Ingliz
- Esperanto
- eston
- fin
- frantsuz
- frizcha
- Galisian
- gruzin
- nemis
- yunoncha
- Gujarati
- Gaiti kreoli
- Hausa
- gavayilik
- ibroniy
- Yo'q
- Miao
- venger
- island
- igbo
- indonez
- irland
- italyancha
- yapon
- yava
- Kannada
- qozoq
- kxmer
- Ruanda
- koreys
- kurd
- qirg'iz
- Mehnat
- lotin
- latviyalik
- litva
- Lyuksemburgcha
- makedon
- malagasy
- malay
- Malayalam
- malta
- maori
- Marathi
- mo'g'ul
- Myanma
- Nepal
- norveg
- norveg
- oksitan
- Pushtu
- forscha
- polyak
- portugal
- panjob
- rumin
- rus
- Samoa
- Shotlandiya gael
- serb
- Ingliz
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- slovak
- sloven
- Somali
- ispancha
- sundan
- suahili
- shvedcha
- Tagalog
- tojik
- Tamil
- tatar
- Telugu
- tay
- turkcha
- turkman
- ukrain
- urdu
- uyg'ur
- o'zbek
- Vetnam
- uels
- Yordam
- Yahudiy
- Yoruba
- Zulu
yangiliklar
Transmission Antenna: Unlocking Wireless Efficiency with Advanced Microstrip Antennas
In today’s connected world, the transmission antenna is a vital element in every communication system, enabling the wireless transfer of data, audio, and video across vast distances. Whether functioning as a tv transmission antenna or a radio transmission antenna, the antenna’s design determines the quality, reliability, and range of signal transmission. Among the many technological innovations in this field, the microstrip antenna has proven to be a breakthrough in compact and high-efficiency antenna engineering. With versions such as the 2.4 GHz microstrip antenna, broadband microstrip patch antenna, and aperture coupled microstrip antenna, microstrip designs have become indispensable in applications ranging from home Wi-Fi to industrial IoT.
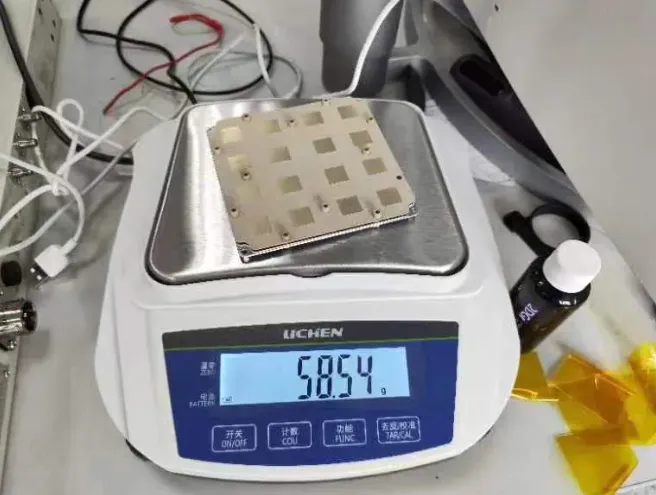

Microstrip Patch Antennas: The Perfect Fit for Modern Transmission
The microstrip patch antenna is especially favored for its low-profile structure and straightforward manufacturing process. Consisting of a radiating patch mounted on a dielectric substrate with a metal ground plane, this type of transmission antenna is easy to integrate into printed circuit boards. It is particularly suitable for applications that require directional radiation, such as wireless base stations, satellite communication terminals, and tv transmission antennas. Its planar form and ability to be mass-produced make it a go-to solution in industries demanding both performance and cost-efficiency.
Versatility of 2.4 GHz Microstrip Patch Antennas
Among the most common frequencies in consumer and industrial devices is the 2.4 GHz ISM band. The 2.4 GHz microstrip antenna and its variant, the 2.4 GHz microstrip patch antenna, are optimized to operate precisely within this frequency range, which powers many wireless systems including Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and smart appliances. These antennas offer excellent gain, compact size, and high efficiency, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. Their easy integration into embedded systems also supports product miniaturization without compromising on performance.
Advancements in Broadband and Aperture Coupled Designs
For applications that demand greater bandwidth or more refined signal control, engineers turn to the broadband microstrip antenna and broadband microstrip patch antenna. These designs incorporate enhancements like stacked patches, multiple resonant modes, or special substrate materials to support wideband performance. They’re ideal for systems that need to operate over a broad frequency range with minimal signal degradation. Meanwhile, the aperture coupled microstrip antenna provides superior isolation between the feed line and radiating patch, resulting in better impedance matching and cleaner signal transmission. This design is particularly useful in precision-driven applications like high-speed data links and advanced radio systems.
In summary, the evolution of the transmission antenna—including tv transmission antennas, radio transmission antennas, and advanced microstrip antennas—has revolutionized how wireless systems are built and perform. The continued refinement of designs like the 2.4 GHz microstrip patch antenna, broadband microstrip antenna, and aperture coupled microstrip antenna ensures that modern communication systems can meet increasing demands for speed, reliability, and compactness. These technologies are foundational in pushing wireless connectivity into new realms of possibility.