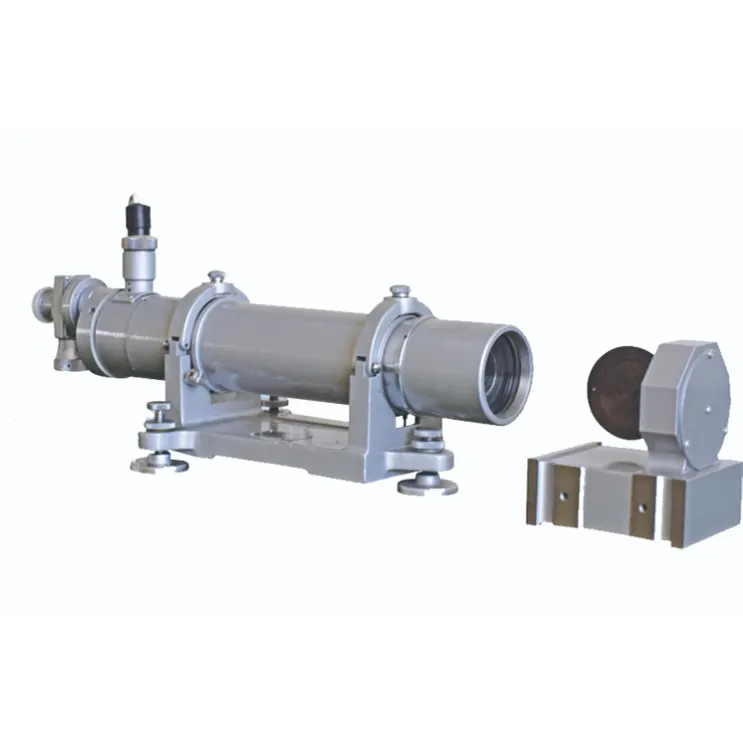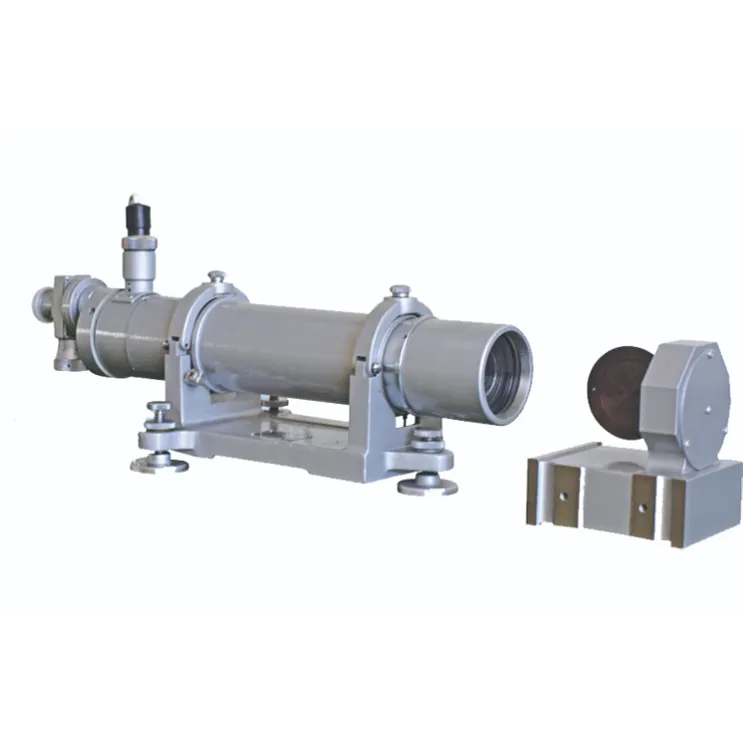
- afrikalik
- alban
- Amhar
- arabcha
- arman
- ozarbayjon
- bask
- belarus
- bengal
- bosniyalik
- bolgar
- katalan
- Sebuano
- Xitoy
- Korsika
- xorvat
- chex
- Daniya
- golland
- Ingliz
- Esperanto
- eston
- fin
- frantsuz
- frizcha
- Galisian
- gruzin
- nemis
- yunoncha
- Gujarati
- Gaiti kreoli
- Hausa
- gavayilik
- ibroniy
- Yo'q
- Miao
- venger
- island
- igbo
- indonez
- irland
- italyancha
- yapon
- yava
- Kannada
- qozoq
- kxmer
- Ruanda
- koreys
- kurd
- qirg'iz
- Mehnat
- lotin
- latviyalik
- litva
- Lyuksemburgcha
- makedon
- malagasy
- malay
- Malayalam
- malta
- maori
- Marathi
- mo'g'ul
- Myanma
- Nepal
- norveg
- norveg
- oksitan
- Pushtu
- forscha
- polyak
- portugal
- panjob
- rumin
- rus
- Samoa
- Shotlandiya gael
- serb
- Ingliz
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- slovak
- sloven
- Somali
- ispancha
- sundan
- suahili
- shvedcha
- Tagalog
- tojik
- Tamil
- tatar
- Telugu
- tay
- turkcha
- turkman
- ukrain
- urdu
- uyg'ur
- o'zbek
- Vetnam
- uels
- Yordam
- Yahudiy
- Yoruba
- Zulu
yangiliklar
Exploring the Power of Multispectral Satellite Imagery for Smarter Earth Observation
As technology reshapes how we observe and understand the world, multispectral satellite imagery stands at the forefront of advanced data collection and analysis. Leveraging data from multiple spectral bands, multispectral satellites are transforming sectors ranging from agriculture to urban development with unprecedented accuracy and scope.
Whether you're an environmental researcher, a city planner, or a space-tech enterprise, access to reliable multi spectral satellite imagery opens the door to insights that traditional imaging methods simply cannot provide.
What Is Multispectral Satellite Imaging?
At its core, a multispectral satellite collects data in multiple wavelength bands, typically including visible, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared. These bands reveal details not visible to the naked eye, such as plant health, moisture content, or thermal variation. Compared to standard photography or RGB satellite images, multi spectral satellite imagery delivers deeper analytical value, making it an indispensable tool in modern Earth observation.
Applications Across Key Industries
Multispectral satellite imagery has become essential for precision agriculture. Farmers and agritech companies use it to monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and detect early signs of disease or stress. The ability to differentiate between healthy and stressed vegetation across various bands enables smarter decision-making and boosts yield.
In environmental monitoring, these satellites help track deforestation, desertification, and coastal erosion. For urban planners, multispectral satellite data enables heat island detection, land use classification, and infrastructure planning with high spatial and temporal resolution.
Disaster management agencies also rely on multi spectral satellite imagery to assess flood extents, wildfire damage, and earthquake impacts—helping allocate resources faster and more effectively.
Advantages of Multispectral Satellites Over Conventional Systems
One of the most notable benefits of multispectral satellite systems is their ability to provide consistent, wide-area coverage over time. This enables time-series analysis, trend detection, and change monitoring at regional or global scales.
Unlike single-band or panchromatic images, multispectral satellite imagery captures diverse surface characteristics, enabling a more holistic understanding of landscapes, infrastructure, and ecosystems. With high revisit rates and increasing resolution, modern platforms deliver timely and actionable data to a broad spectrum of users.
From Raw Data to Smart Insights
Accessing multi spectral satellite imagery is no longer a challenge limited to government agencies or research labs. Thanks to commercial providers and cloud-based processing platforms, businesses and smaller organizations can now purchase, analyze, and visualize multispectral data with ease.
Advanced algorithms powered by machine learning and AI further amplify the value of multispectral satellite data. These tools can classify land cover, detect anomalies, and even predict environmental trends—all in near-real time.
Future Outlook
As sensor technology advances and costs decline, multispectral satellite systems are becoming more compact, affordable, and accessible. CubeSats and small satellite constellations equipped with multispectral payloads are extending coverage and improving temporal resolution, making near-real-time global monitoring a reality.
As the demand for sustainability, resilience, and informed decision-making grows, the role of multispectral satellite imagery will only expand.
Conclusion
Multispectral satellite technology is no longer just a scientific curiosity—it is a critical component of modern intelligence across agriculture, environment, urban planning, and disaster response. The rich, multi-band data captured through multi spectral satellite imagery is enabling a more informed, data-driven approach to managing our planet.
Whether you're analyzing crop vitality or monitoring deforestation, multispectral satellite imagery offers the clarity and precision needed to see the bigger picture.











