- africký
- albánsky
- amharčina
- arabčina
- arménsky
- azerbajdžanský
- baskický
- bieloruský
- bengálsky
- bosniansky
- bulharčina
- katalánsky
- Cebuano
- Čína
- korzické
- chorvátsky
- český
- dánčina
- holandský
- angličtina
- Esperanto
- estónsky
- fínsky
- francúzsky
- frízsky
- Haličský
- gruzínsky
- nemecký
- grécky
- Gudžarátčina
- haitská kreolčina
- Hausa
- havajský
- hebrejčina
- Nie
- Miao
- maďarský
- islandský
- igbo
- indonézsky
- írsky
- taliansky
- japončina
- jávsky
- Kannada
- kazašský
- khmérsky
- Rwanda
- kórejský
- kurdský
- kirgizský
- práce
- latinčina
- lotyšský
- litovský
- luxemburský
- macedónsky
- malgašský
- malajčina
- malajálamčina
- maltčina
- Maori
- maráthčina
- mongolský
- Mjanmarsko
- nepálsky
- nórsky
- nórsky
- okcitánsky
- paštčina
- perzský
- poľský
- portugalčina
- pandžábsky
- rumunský
- ruský
- Samoan
- škótska galčina
- srbský
- angličtina
- Shona
- Sindhi
- sinhálčina
- slovenský
- slovensky
- somálsky
- španielčina
- sundánsky
- svahilčina
- švédsky
- Tagalog
- tadžický
- tamilčina
- tatársky
- telugčina
- thajčina
- turecký
- turkménskym
- Ukrajinčina
- urdčina
- ujgurské
- uzbecký
- Vietnamci
- waleský
- Pomoc
- jidiš
- Yoruba
- Zulu
správy
Revolutionizing Earth Observation With Remote Sensing And Satellite Imagery
In the age of digital transformation, remote sensing and satellite imagery have become indispensable tools for monitoring environmental changes, supporting urban development, and informing policy decisions. From high-definition terrain mapping to economic forecasting using night time light satellite imagery, these technologies offer an unparalleled view of our planet. As demand grows for real-time, accurate, and diverse Earth observation solutions, the integration of satellite remote sensing data has become central to strategic planning across industries.
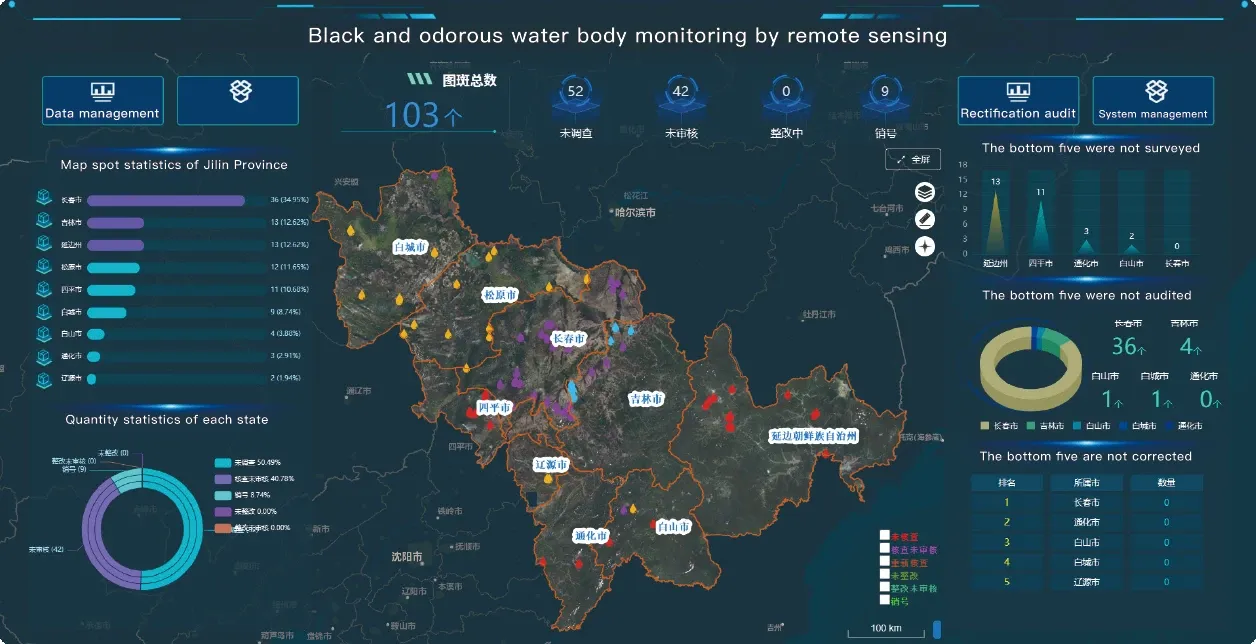
Remote Sensing Satellite Image: The Foundation of Modern Earth Observation
The remote sensing satellite image is more than just a photograph from space—it is a layered dataset that reveals patterns, anomalies, and trends invisible to the naked eye. From identifying agricultural stress to detecting illegal deforestation, satellite remote sensing data enables analysts to act on early indicators of change. The resolution, frequency, and scope of these images continue to improve with each generation of satellites. Moreover, remotely sensed satellite imagery can be tailored to specific missions, whether monitoring desertification or tracking urban sprawl.
Panchromatic Satellite Imagery and Detail Enhancement
High-detail analysis often depends on panchromatic satellite imagery, which offers superior spatial resolution by capturing imagery in a single, wide-spectrum black-and-white band. This imagery is particularly useful for infrastructure planning, road network identification, and detailed topographical mapping. When merged with multispectral data through pan-sharpening techniques, panchromatic satellite imagery enhances the visual clarity and interpretive value of remote sensing and satellite imagery datasets. This fusion technique makes it possible to analyze both spectral and spatial details simultaneously, greatly benefiting sectors like defense, mining, and agriculture.
Night Time Light Satellite Imagery and Socioeconomic Insights
Few tools offer as direct a link between satellite data and economic activity as night time light satellite imagery. This data captures human activity patterns after dark—from streetlights and traffic to industrial operations—offering insights into urbanization, disaster recovery, and development levels. Governments and international organizations use night time light satellite imagery to track energy distribution, estimate population changes, and assess regional economic performance. Combined with high resolution remote sensing images, this nighttime data delivers a comprehensive understanding of human impacts on the planet.
The Growing List of High Resolution Remote Sensing Satellites
A continuously expanding high resolution remote sensing satellites list reflects the rapid innovation in Earth observation technology. These satellites provide imagery at sub-meter resolutions, allowing for precise monitoring of even small-scale changes. Whether it’s measuring crop health, planning new highways, or assessing post-disaster conditions, high resolution remote sensing images are essential. The availability of these satellites has democratized access to premium-quality satellite remote sensing data, making it an essential asset for both governments and commercial users.
Conclusion: The Future of Remote Sensing and Satellite Imagery
With rapid technological advancement and increased satellite launches, remote sensing and satellite imagery are set to play an even more significant role in global development. The use of remotely sensed satellite imagery, combined with tools like panchromatic satellite imagery and night time light satellite imagery, provides a multi-dimensional perspective on Earth’s surface. As organizations seek smarter ways to analyze and react to changes, satellite remote sensing data emerges as a cornerstone of informed decision-making. From climate science to infrastructure planning, this technology is not just observing the world—it’s helping to shape its future.